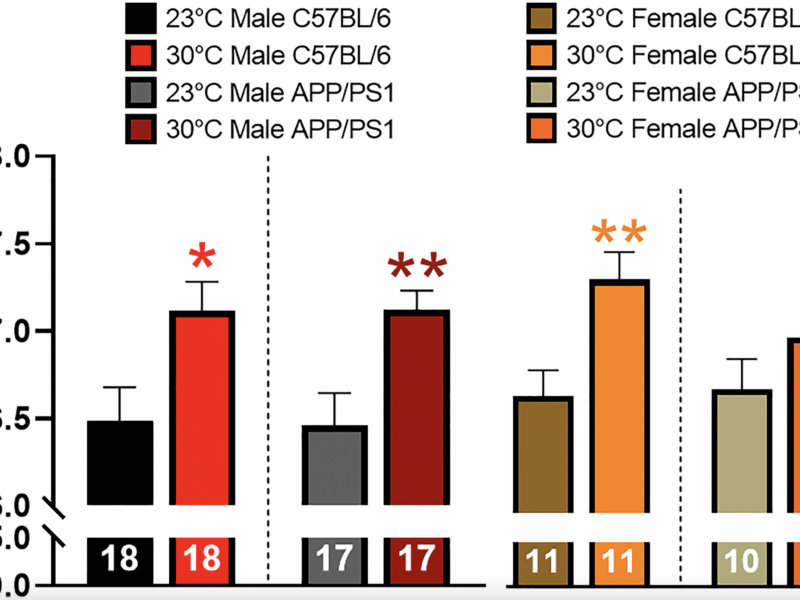
A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as “Aging (Albany NY)” and “Aging-US” by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 21 on November 29, 2024, entitled, “Thermotherapy has sexually dimorphic responses in APP/PS1 mice.”
Aging (Aging-US) Authors
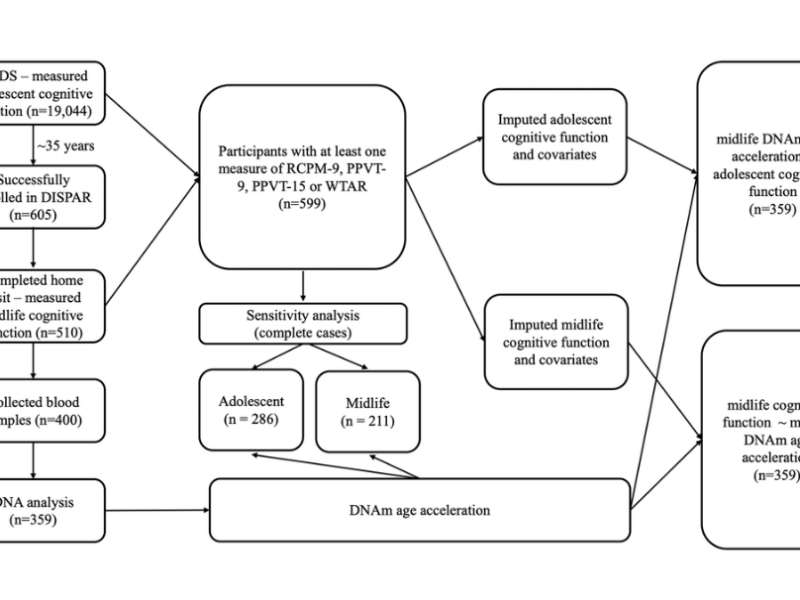
PRESS RELEASE: A new research paper was published in Aging’s Volume 16, Issue 11, entitled, “Associations of childhood, adolescence, and midlife cognitive function with DNA methylation age acceleration in midlife.”
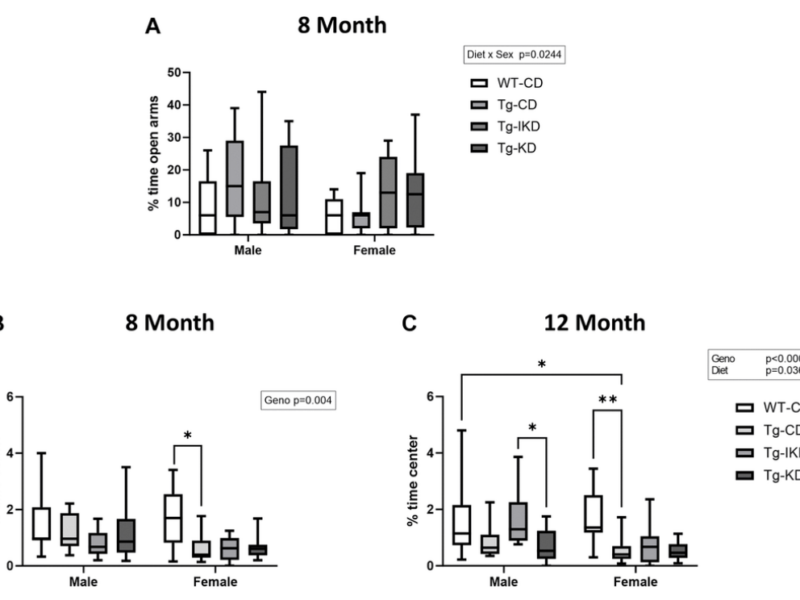
PRESS RELEASE: A new research paper was published in Aging’s Volume 16, Issue 7, entitled, “The impact of continuous and intermittent ketogenic diets on cognitive behavior, motor function, and blood lipids in TgF344-AD rats.”
PRESS RELEASE: A new research paper was published in Aging’s Volume 16, Issue 6, entitled, “Geraniol attenuates oxidative stress and neuroinflammation-mediated cognitive impairment in D galactose-induced mouse aging model.”
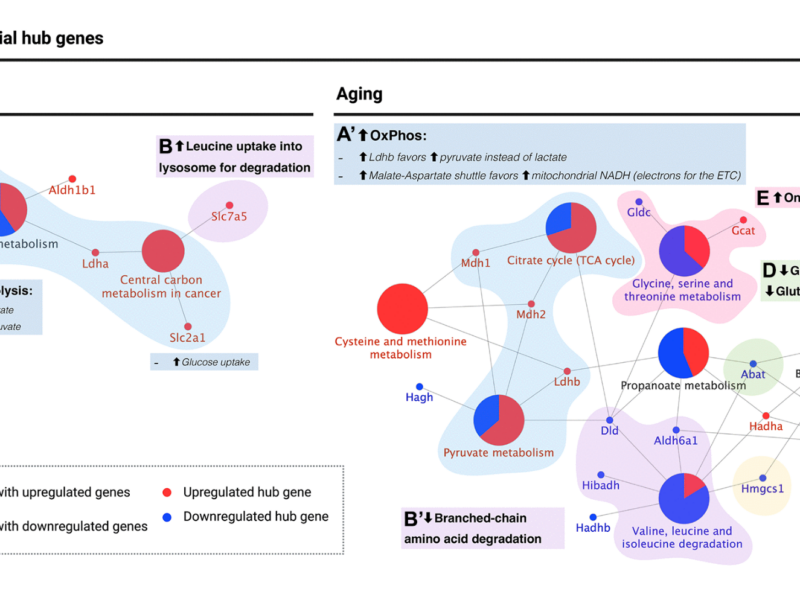
PRESS RELEASE: A new research paper was published in Aging’s Volume 15, Issue 19, entitled, “Metabolic switch in the aging astrocyte supported via integrative approach comprising network and transcriptome analyses.”
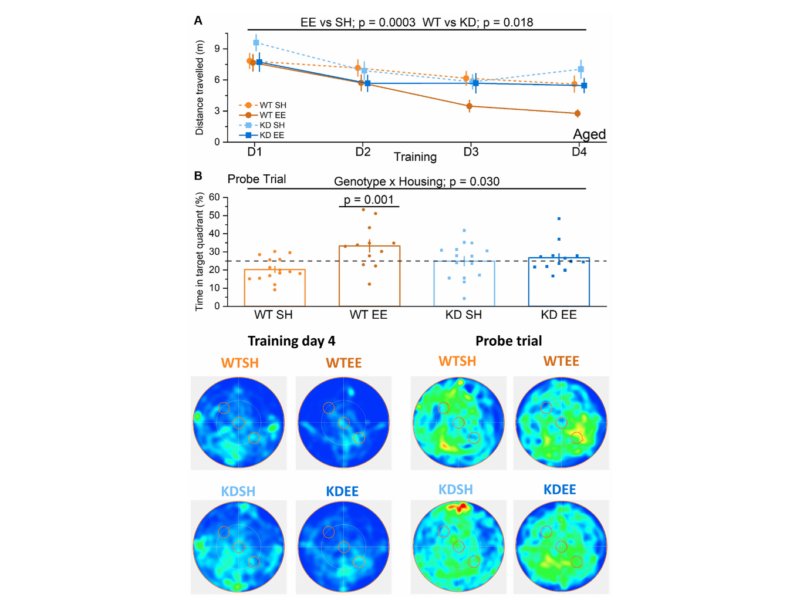
PRESS RELEASE: A new research paper was published in Aging’s Volume 15, Issue 13, entitled, “MSK1 is required for the beneficial synaptic and cognitive effects of enriched experience across the lifespan.”
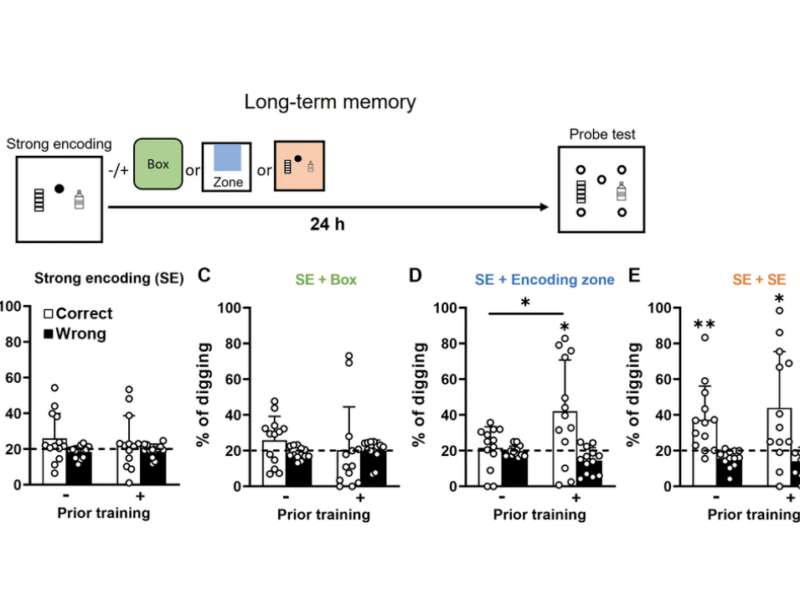
PRESS RELEASE: A new research paper was published in Aging’s Volume 15, Issue 13, entitled, “Cognitive rescue in aging through prior training in rats.”

PRESS RELEASE: A new editorial paper was published in Aging’s Volume 15, Issue 12, entitled, “Advancing screening for cognitive impairment: the memtrax continuous recognition test.”
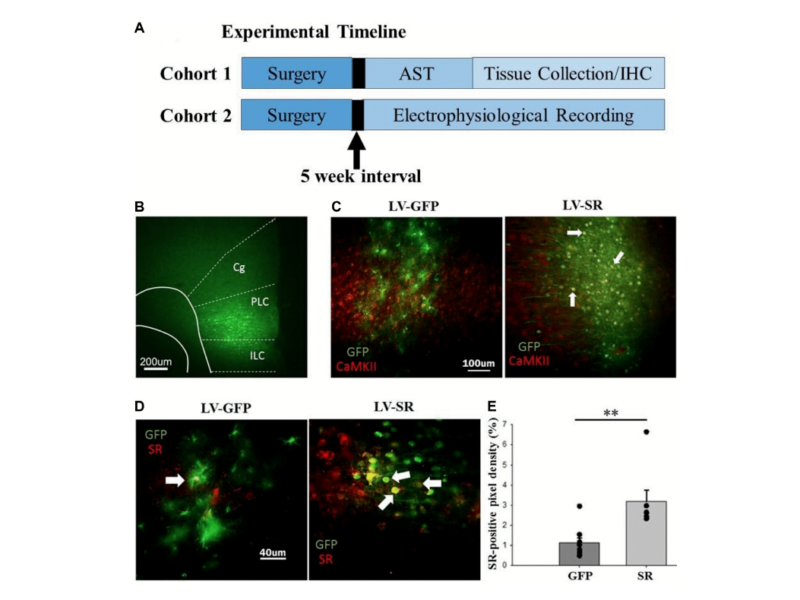
PRESS RELEASE: A new research paper was published in Aging’s Volume 15, Issue 7, entitled, “Viral vector-mediated upregulation of serine racemase expression in medial prefrontal cortex improves learning and synaptic function in middle age rats.”
PRESS RELEASE: Researchers from the University of Barcelona published a new editorial in Aging’s Volume 15, Issue 4, entitled, “Cognitive aging and dementia prevention: the time for psychology?”