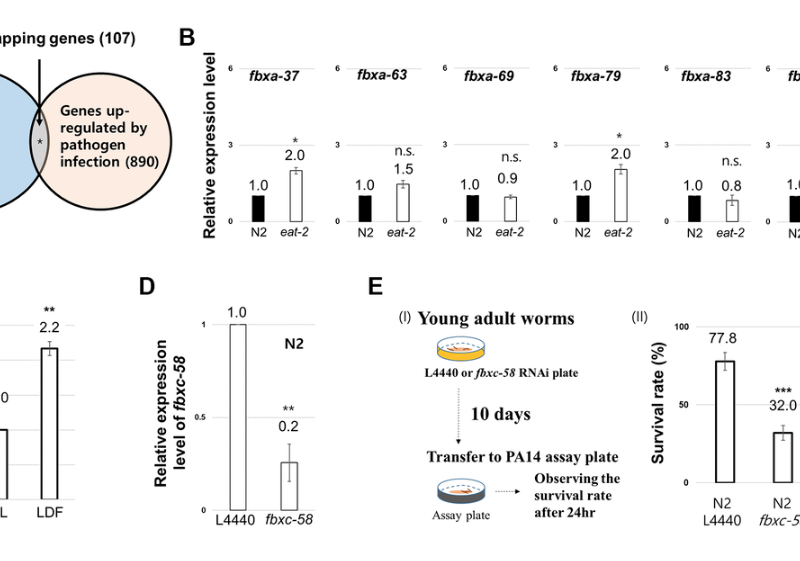
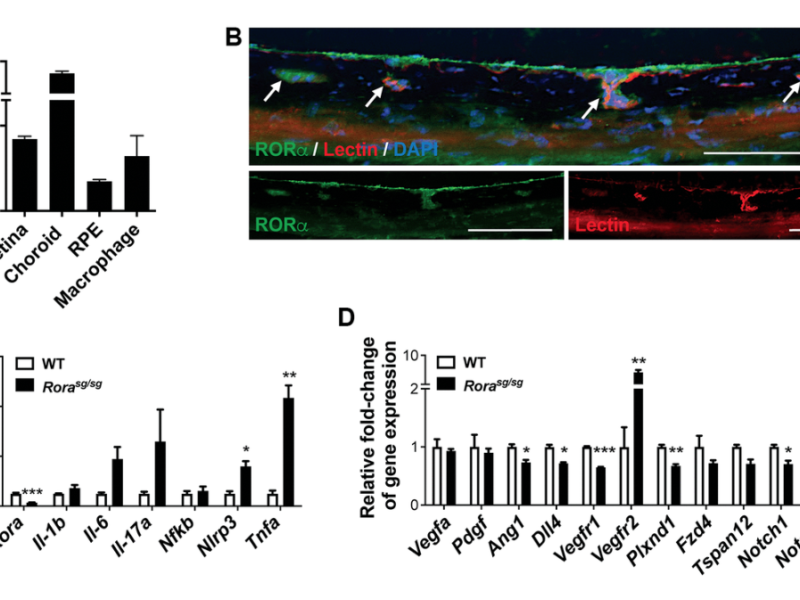
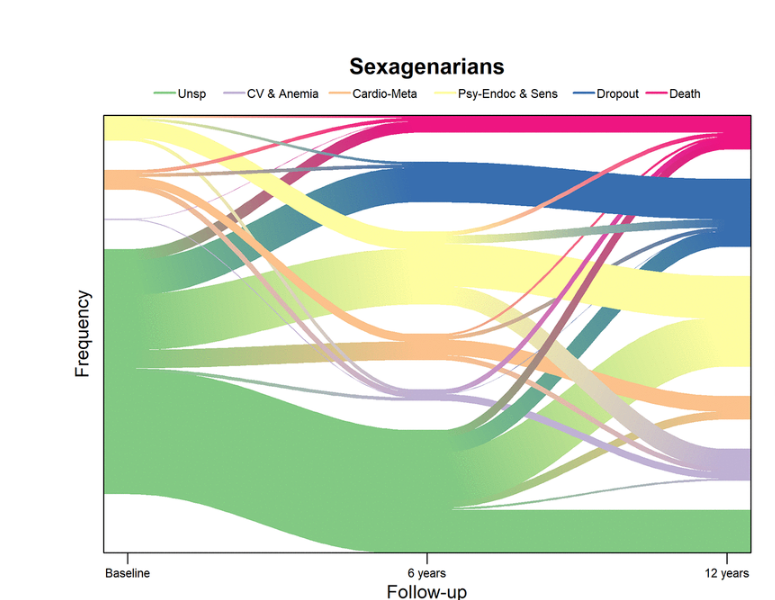
Aging (Aging-US) Authors
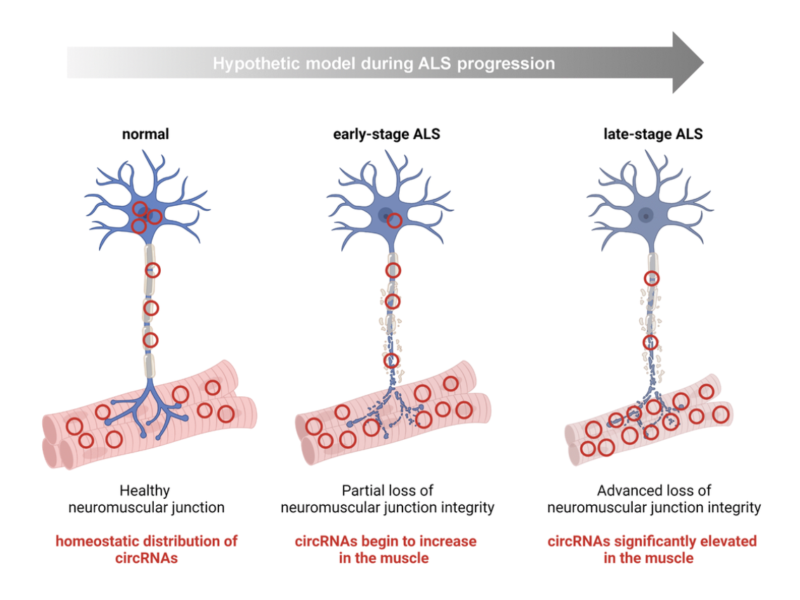
PRESS RELEASE: On December 30, 2022, Aging published a new research paper entitled, “Transcriptomic analysis of human ALS skeletal muscle reveals a disease-specific pattern of dysregulated circRNAs.”
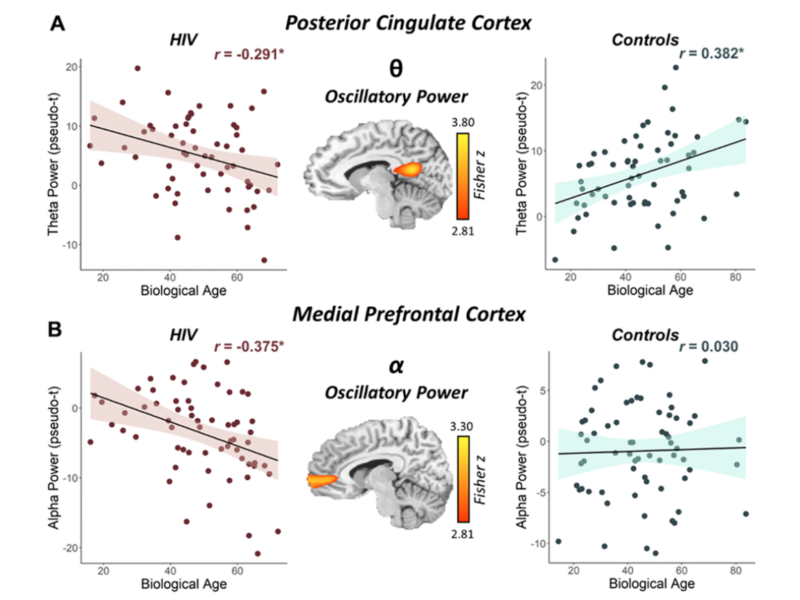
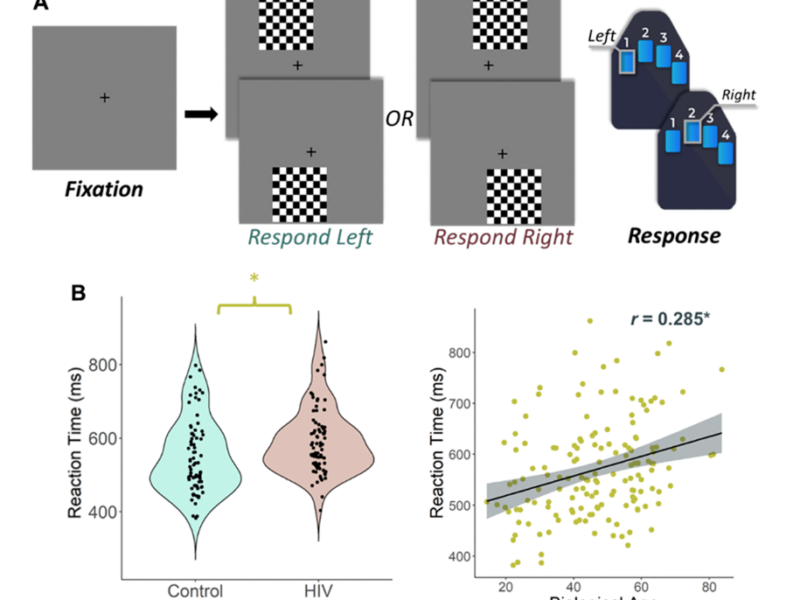
PRESS RELEASE: A new research paper was published in Aging’s Volume 14, Issue 24, entitled, “Epigenetic aging is associated with aberrant neural oscillatory dynamics serving visuospatial processing in people with HIV.”
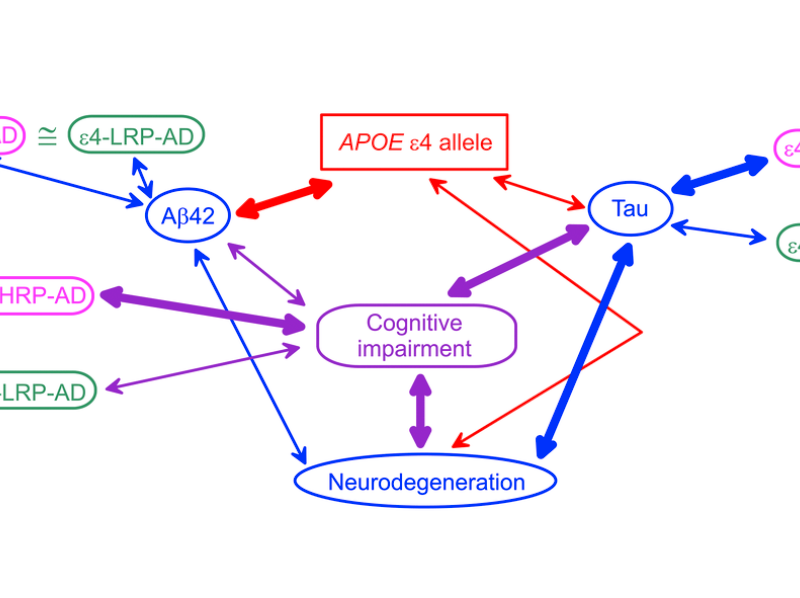
PRESS RELEASE: A new research paper was published on the cover of Aging’s Volume 14, Issue 24, entitled, “Associations of the APOE ε2 and ε4 alleles and polygenic profiles comprising APOE-TOMM40-APOC1 variants with Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers.”
Capturing the genetic architecture of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is challenging because of the complex interplay of genetic and non-genetic factors in its etiology. It has been suggested that AD biomarkers may improve the characterization of AD pathology and its genetic architecture…

PRESS RELEASE: A new research paper was published in Aging’s Volume 14, Issue 23, entitled, “DNA methylation-based measures of biological aging and cognitive decline over 16-years: preliminary longitudinal findings in midlife.”

PRESS RELEASE: A new research paper was published in Aging’s Volume 14, Issue 23, entitled, “White matter hyperintensity load is associated with premature brain aging.”