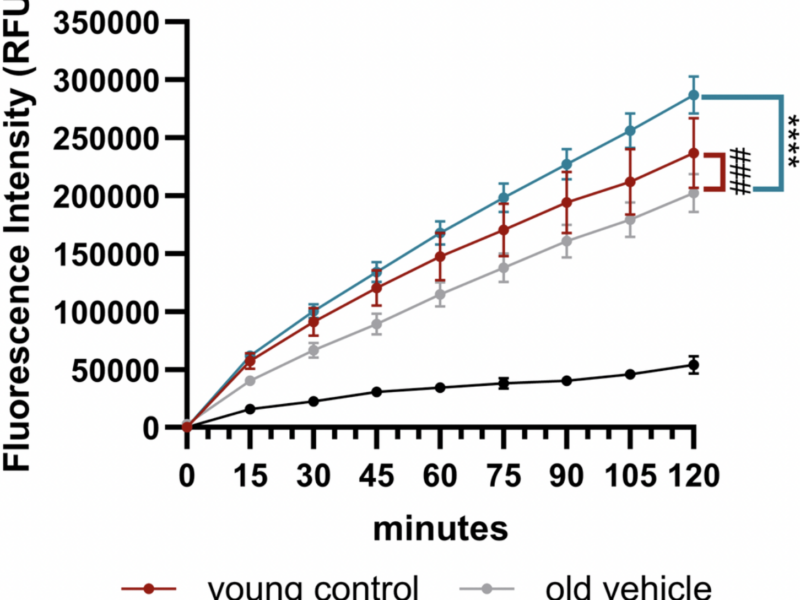
A new research paper was published in Aging (Aging-US) on January 31, 2025, in Volume 17, Issue 2, titled “Cysteinyl leukotriene receptor 1 modulates retinal immune cells, vascularity and proteolytic activity in aged mice.”
Aging-US Authors

Dr. Julia Sidorova from the University of Washington joins host Dr. Evgeniy Galimov to discuss her co-authored research paper from Volume 16, Issue 20 of Aging (Aging-US), titled “Werner syndrome RECQ helicase participates in and directs maintenance of the protein complexes of constitutive heterochromatin in proliferating human cells.”
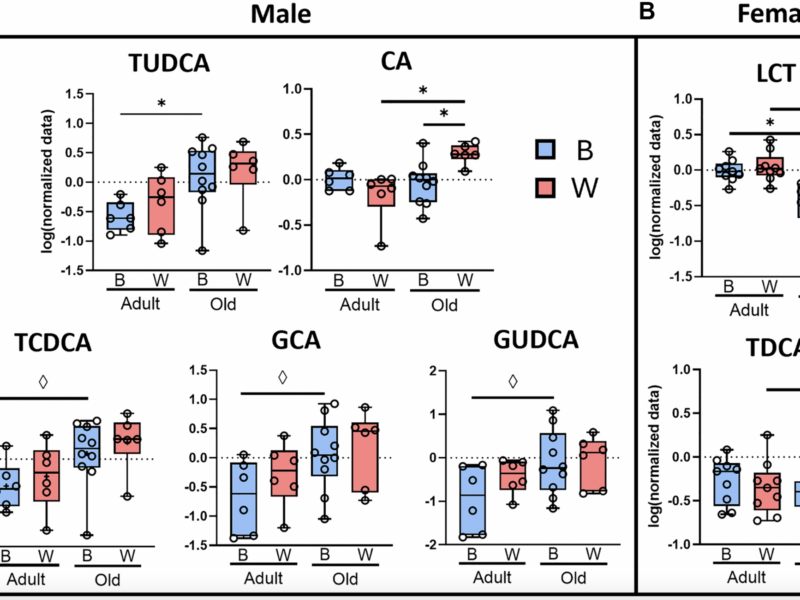
A new research paper was published in Aging (Aging-US) on February 27, 2025, in Volume 17, Issue 2, titled “Age, sex, and mitochondrial-haplotype influence gut microbiome composition and metabolites in a genetically diverse rat model.”
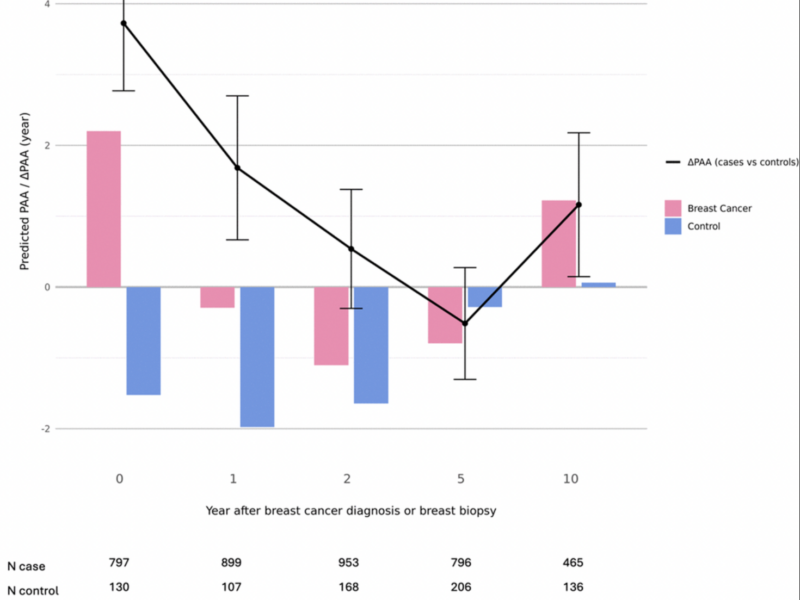
A new research paper was published by Aging (Aging-US) on March 7, 2025, titled “Accelerated aging associated with cancer characteristics and treatments among breast cancer survivors.”

Impact Journals (Aging’s publisher) is pleased to announce its participation as an exhibitor at theAmerican Association for Cancer Research (AACR) Annual Meeting 2025. The meeting is scheduled for April 25-30, 2025, at the McCormick Place Convention Center in Chicago, Illinois.
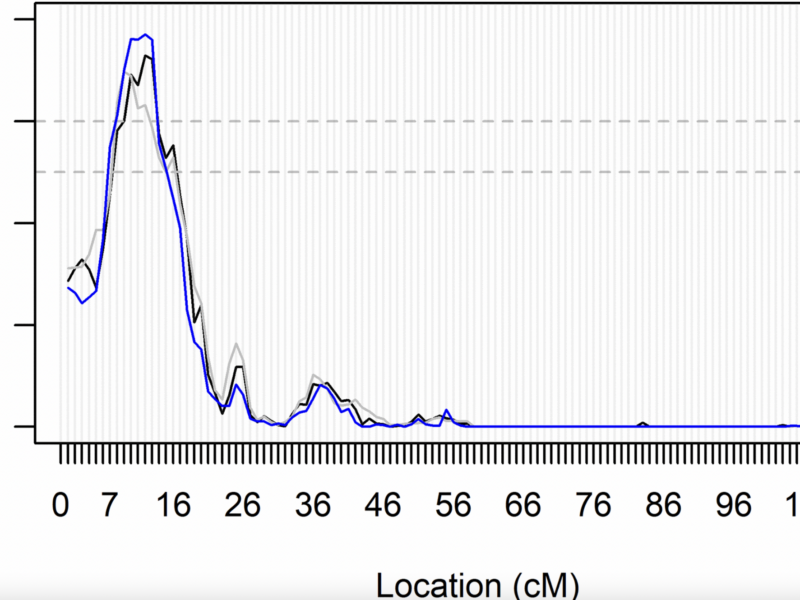
A new research paper was published in Aging (Aging-US) on February 25, 2025, Volume 17, Issue 2, titled “Epidemiology and genetic determination of measures of peripheral vascular health in the Long Life Family Study.”
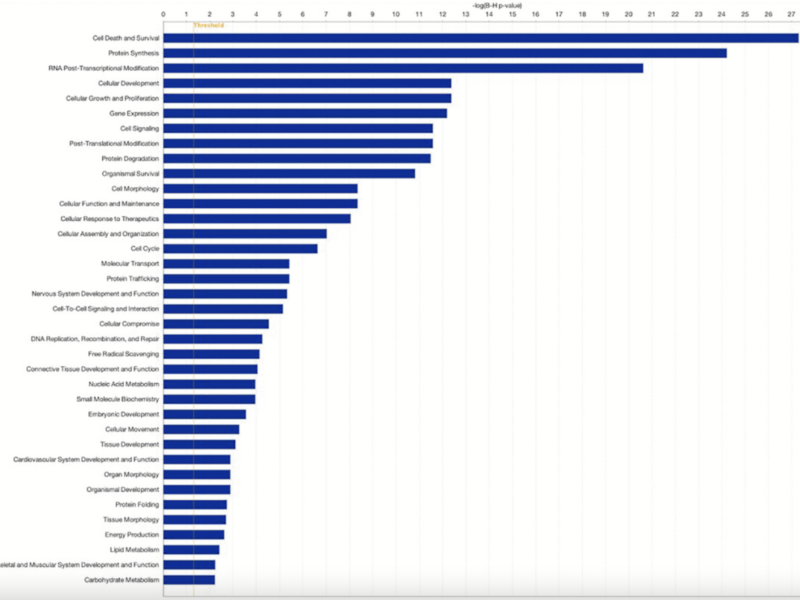
A new research paper was published in Aging (Aging-US) on February 18, 2025, Volume 17, Issue 2, titled “Transcriptomic landscape of cumulus cells from patients <38 years old with a history of poor ovarian response (POR) treated with platelet-rich plasma (PRP).”
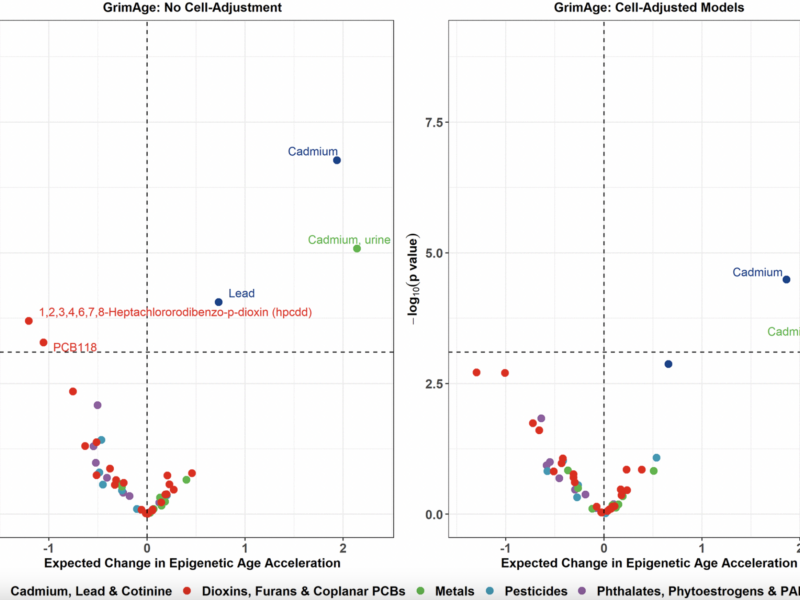
A new research paper was published in Aging (Aging-US) on February 11, 2025, Volume 17, Issue 2, titled “Exposome-wide association study of environmental chemical exposures and epigenetic aging in the national health and nutrition examination survey.”
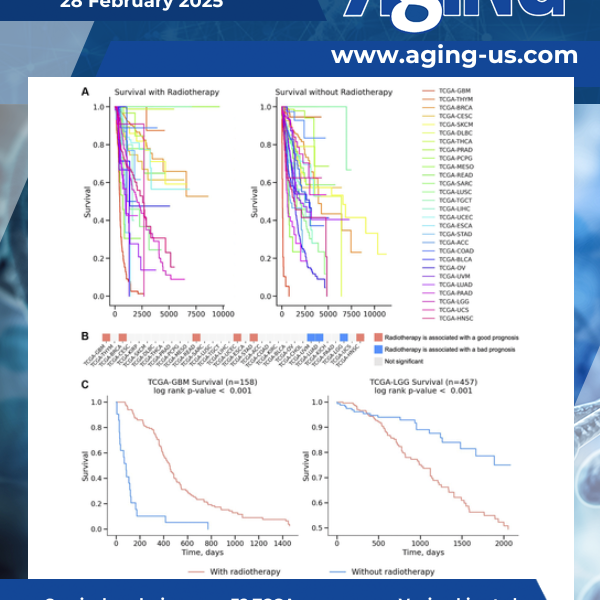
A new research paper was published in Aging (Aging-US) on February 27, 2025, as the cover of Volume 17, Issue 2, titled “Variability in radiotherapy outcomes across cancer types: a comparative study of glioblastoma multiforme and low-grade gliomas.”
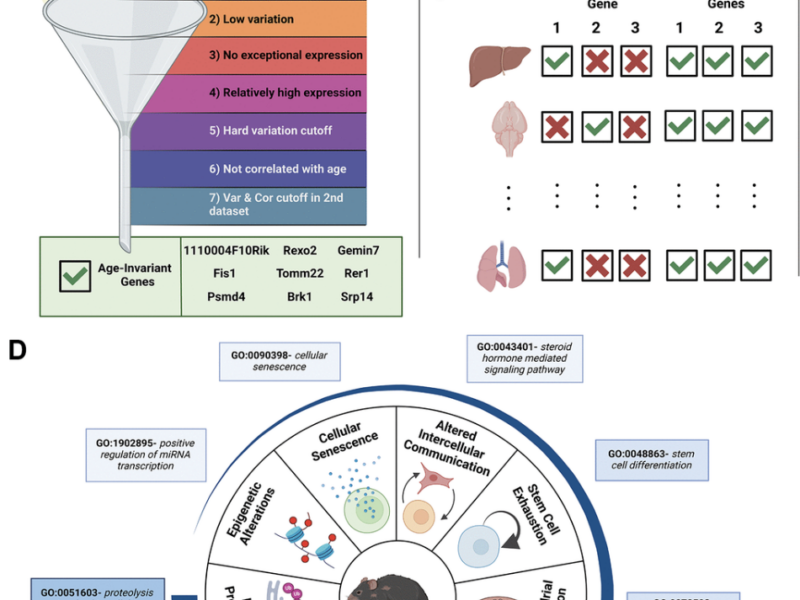
A new research paper was published in Aging (Aging-US) on January 27, 2025, in Volume 17, Issue 1, titled “Age-invariant genes: multi-tissue identification and characterization of murine reference genes.”