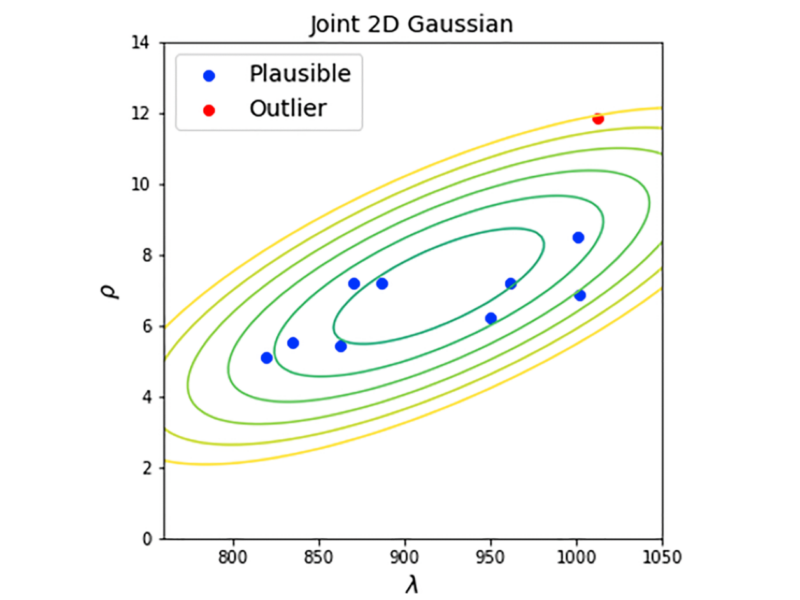
PRESS RELEASE: A new research perspective was published in Aging’s Volume 16, Issue 4, entitled, “On standardization of controls in lifespan studies.”
Aging (Aging-US) Authors
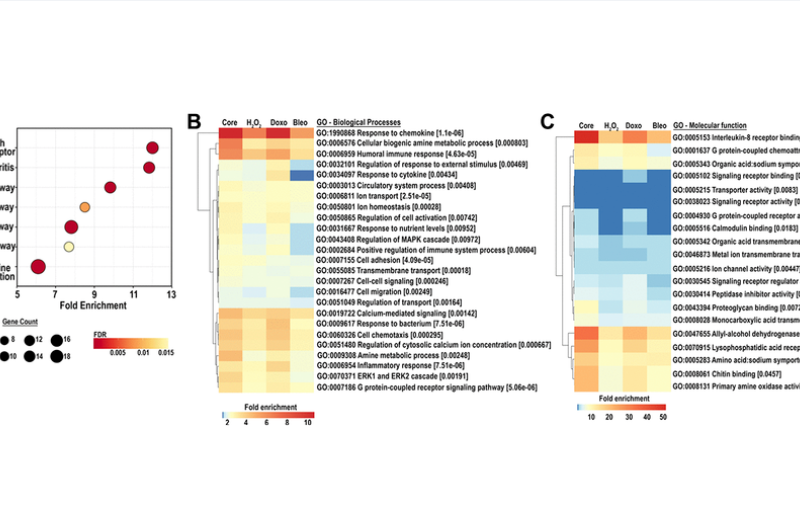
PRESS RELEASE: A new research paper was published on the cover of Aging’s Volume 16, Issue 4, entitled, “Mapping the core senescence phenotype of primary human colon fibroblasts.”
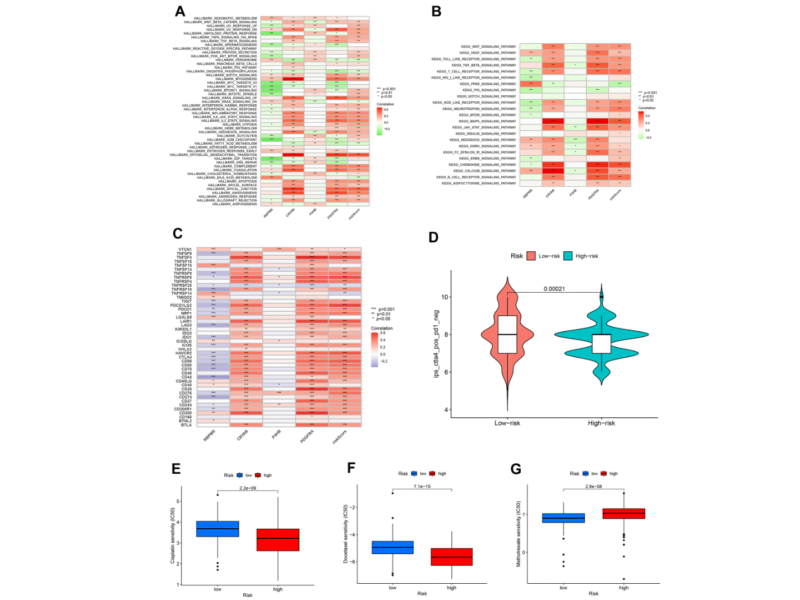
PRESS RELEASE: A new research paper was published in Aging’s Volume 16, Issue 3, entitled, “Prognostic model development and molecular subtypes identification in bladder urothelial cancer by oxidative stress signatures.”
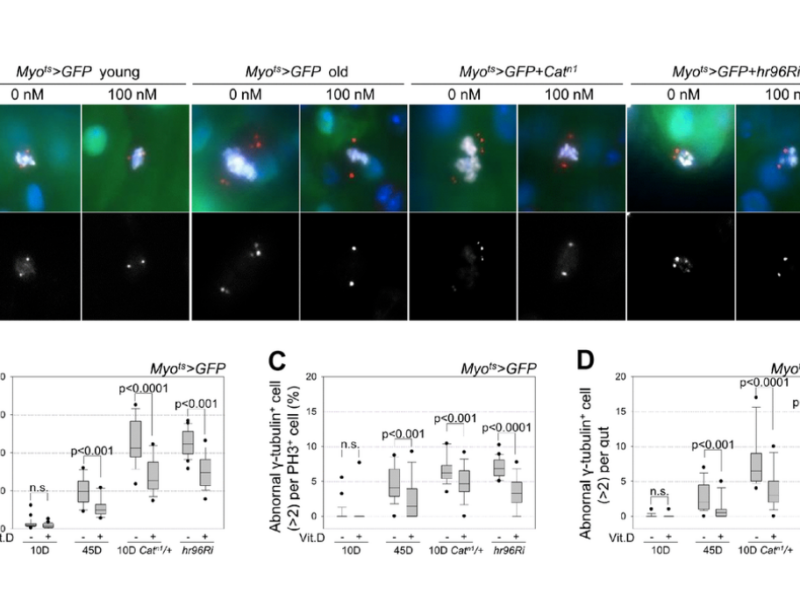
PRESS RELEASE: A new research paper was published in Aging’s Volume 16, Issue 3, entitled, “The anti-aging effect of vitamin D and vitamin D receptor in Drosophila midgut.”
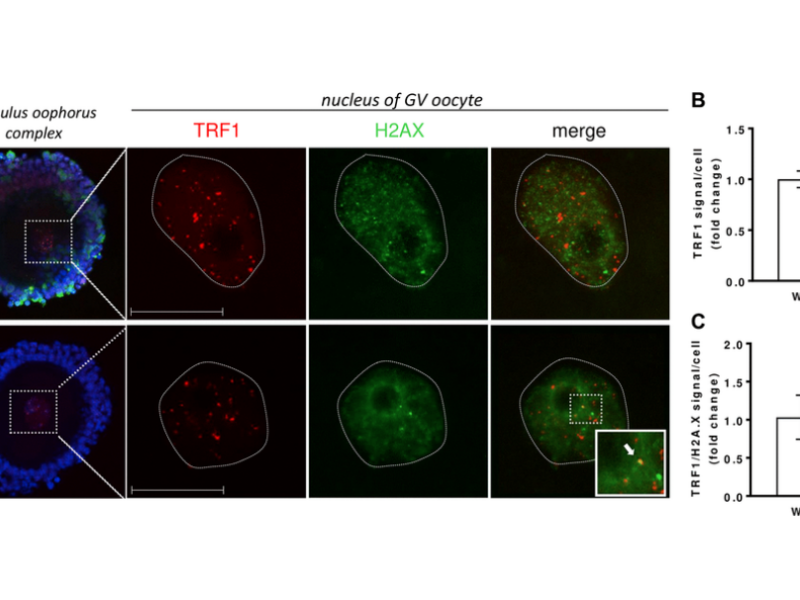
PRESS RELEASE: A new research paper was published in Aging’s Volume 16, Issue 3, entitled, “Disruption of mitochondrial unfolded protein response results in telomere shortening in mouse oocytes and somatic cells.”
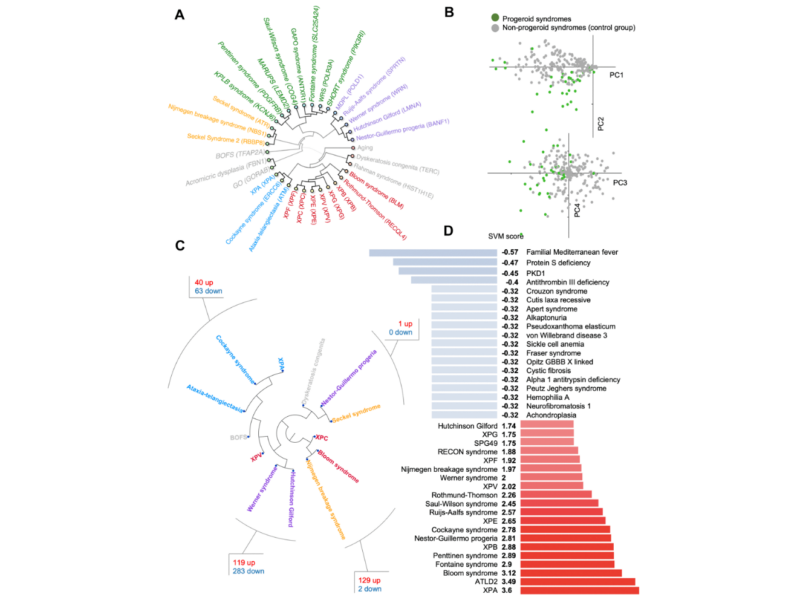
PRESS RELEASE: A new research paper was published in Aging’s Volume 16, Issue 3, entitled, “Defining the progeria phenome.”
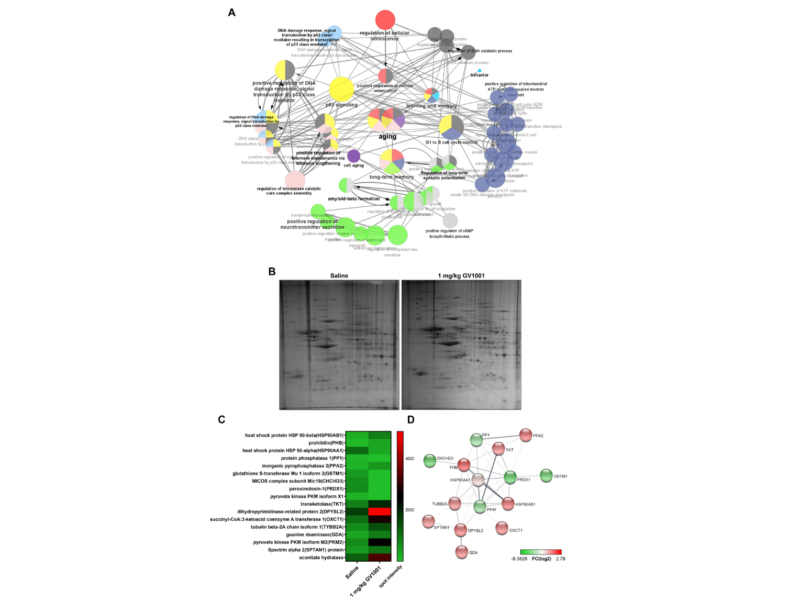
PRESS RELEASE: A new research paper was published on the cover of Aging’s Volume 16, Issue 3, entitled, “GV1001 reduces neurodegeneration and prolongs lifespan in 3xTg-AD mouse model through anti-aging effects.”
![Figure 7. Schematic diagram illustrates the process whereby IL-17 treatment promotes IL-18 production in OASFs [osteoarthritis synovial fibroblasts].](https://aging-us.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/Screen-Shot-2024-02-13-at-11.52.53-AM-800x600.png)
PRESS RELEASE: A new research paper was published in Aging’s Volume 16, Issue 2, entitled, “IL-17 promotes IL-18 production via the MEK/ERK/miR-4492 axis in osteoarthritis synovial fibroblasts.”
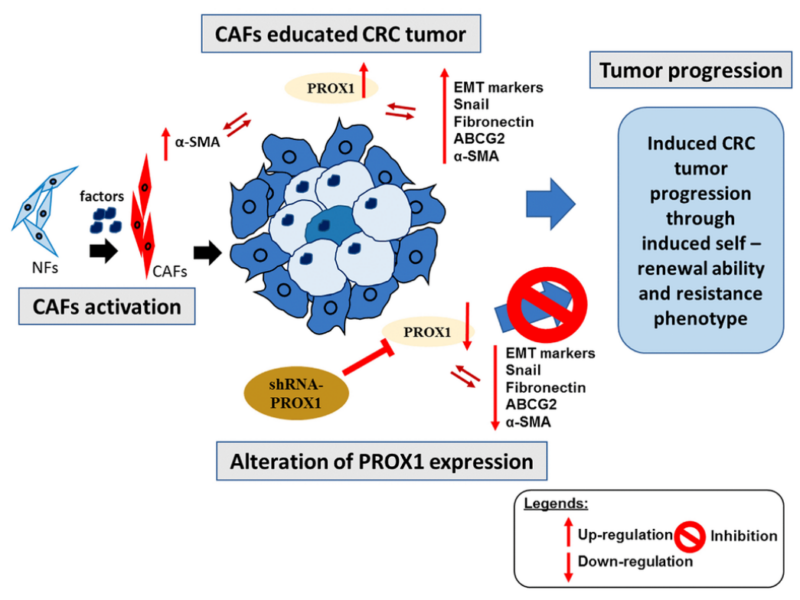
PRESS RELEASE: A new research paper was published in Aging’s Volume 16, Issue 2, entitled, “PROX1 interaction with α-SMA-rich cancer-associated fibroblasts facilitates colorectal cancer progression and correlates with poor clinical outcomes and therapeutic resistance.”
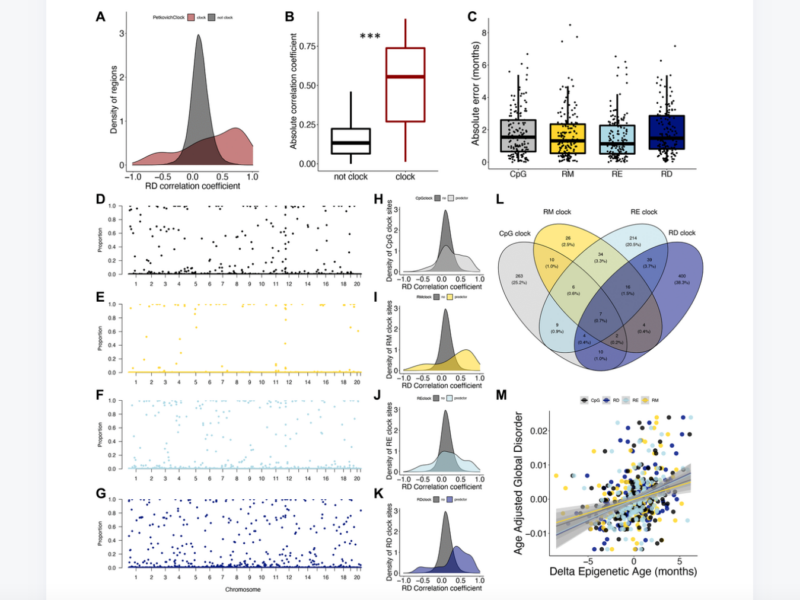
PRESS RELEASE: A new research paper was published in Aging’s Volume 16, Issue 2, entitled, “Epigenetic drift underlies epigenetic clock signals, but displays distinct responses to lifespan interventions, development, and cellular dedifferentiation.”