PRESS RELEASE: A new editorial paper was published in Aging’s Volume 15, Issue 12, entitled, “Advancing screening for cognitive impairment: the memtrax continuous recognition test.”
Aging (Aging-US) Authors
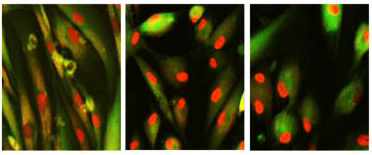
PRESS RELEASE: On July 12, 2023, a new research paper was published in Aging, titled, “Chemically induced reprogramming to reverse cellular aging.”
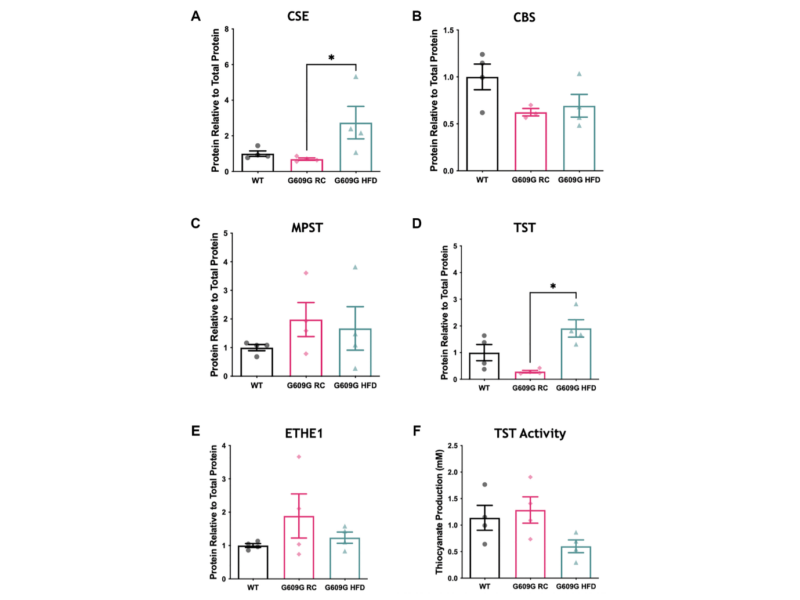
PRESS RELEASE: A new research paper was published in Aging’s Volume 15, Issue 12, entitled, “Hepatic hydrogen sulfide levels are reduced in mouse model of Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome.”
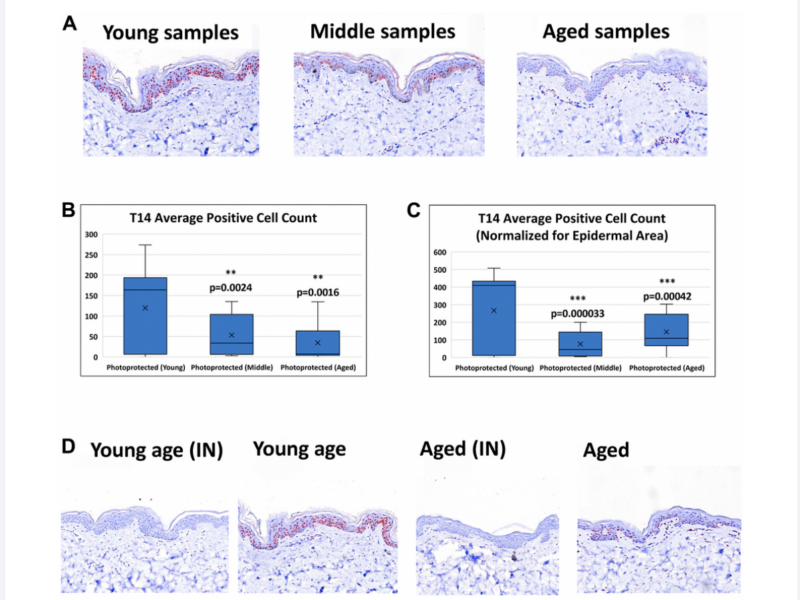
PRESS RELEASE: A new research paper was published in Aging’s Volume 15, Issue 12, entitled, “A novel peptide ‘T14’ reflects age and photo-aging in human skin.”
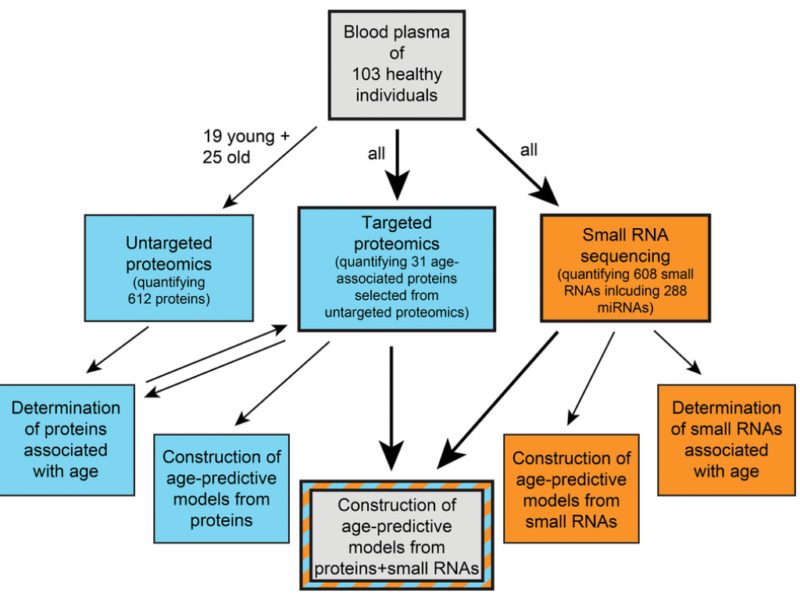
PRESS RELEASE: A new research paper was published on the cover of Aging’s Volume 15, Issue 12, entitled, “Age prediction from human blood plasma using proteomic and small RNA data: a comparative analysis.”
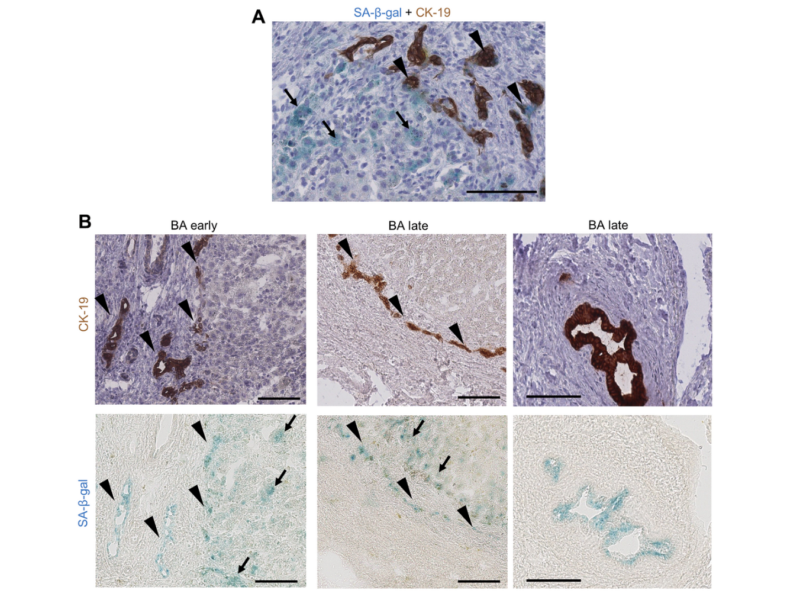
PRESS RELEASE: A new research paper was published in Aging’s Volume 15, Issue 11, entitled, “Senescence and senotherapies in biliary atresia and biliary cirrhosis.”
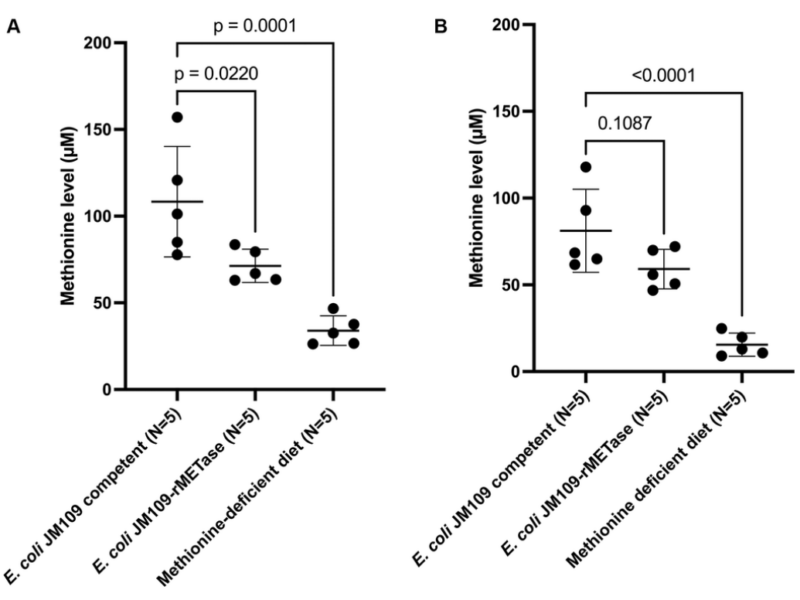
PRESS RELEASE: A new research paper was published in Aging’s Volume 15, Issue 11, entitled, “Old-age-induced obesity reversed by a methionine-deficient diet or oral administration of recombinant methioninase-producing Escherichia coli in C57BL/6 mice.”
In this year’s Ride for Roswell, Aging and Team Open Access contributed to raising $5.6 MILLION (and counting) for cancer research.
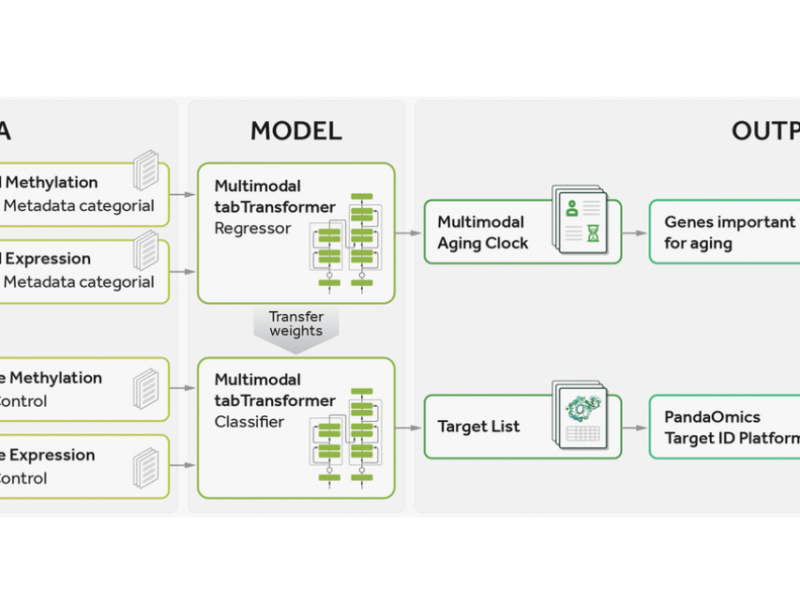
PRESS RELEASE: A new research paper was published in Aging’s Volume 15, Issue 11, entitled, “Precious1GPT: multimodal transformer-based transfer learning for aging clock development and feature importance analysis for aging and age-related disease target discovery.”

Aging’s publisher, Impact Journals, is sponsoring Team Open Access in the annual cycling event to end cancer: The Ride for Roswell.
