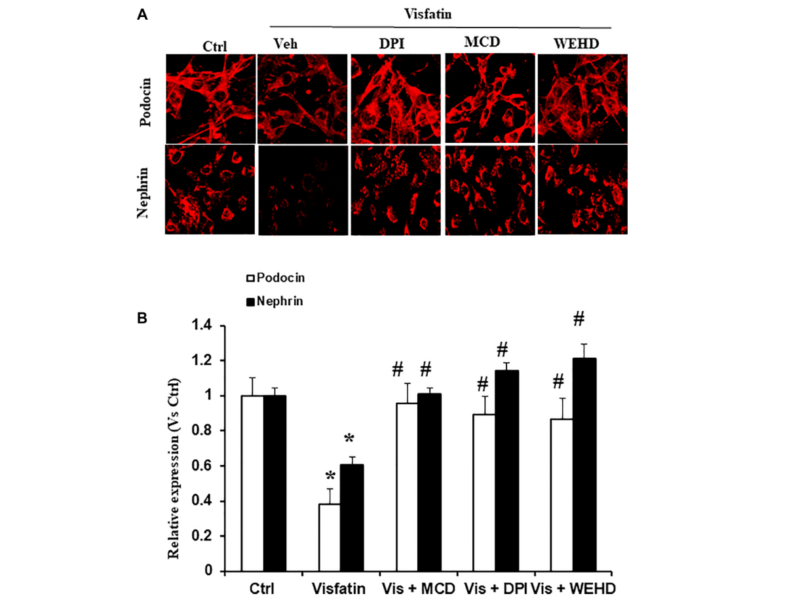
PRESS RELEASE: A new research paper was published in Aging’s Volume 15, Issue 22, entitled, “Contribution of membrane raft redox signalling to visfatin-induced inflammasome activation and podocyte injury.”
Aging (Aging-US) Authors
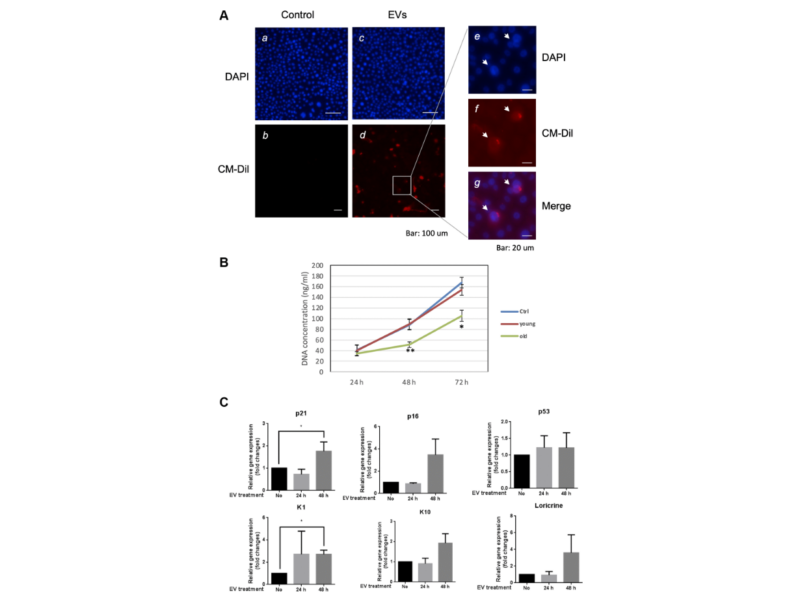
PRESS RELEASE: A new research paper was published on the cover of Aging’s Volume 15, Issue 22, entitled, “Chronological aging impacts abundance, function and microRNA content of extracellular vesicles produced by human epidermal keratinocytes.”
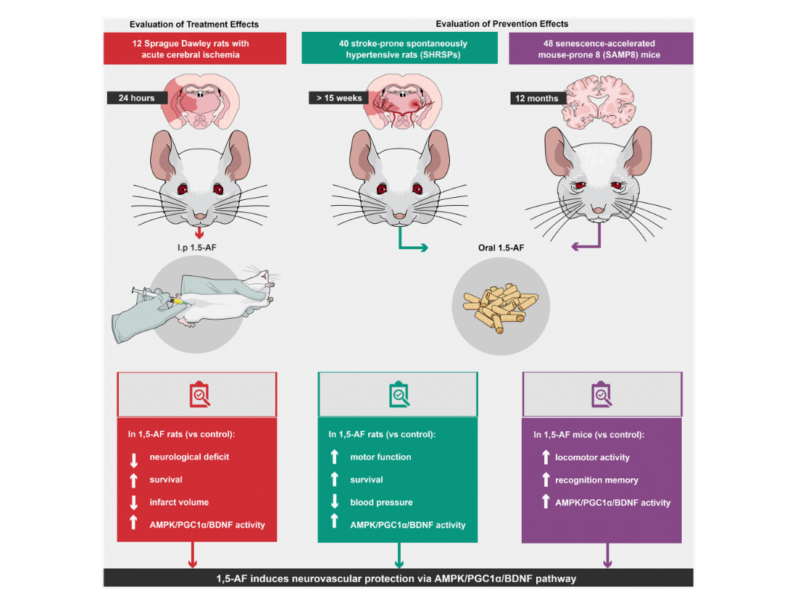
PRESS RELEASE: A new research paper was published in Aging’s Volume 15, Issue 21, entitled, “1,5-anhydro-D-fructose induces anti-aging effects on aging-associated brain diseases […]”
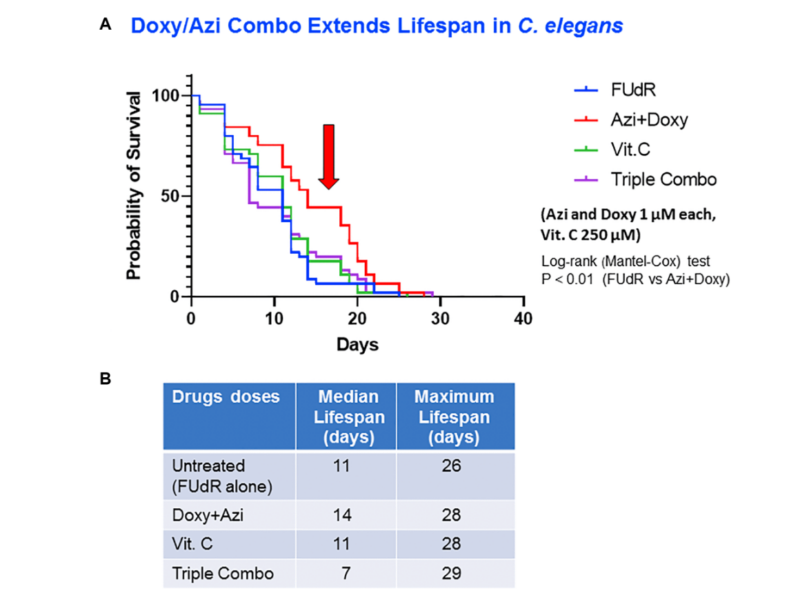
PRESS RELEASE: A new research paper was published in Aging’s Volume 15, Issue 21, entitled, “Antibiotics that target mitochondria extend lifespan in C. elegans.”
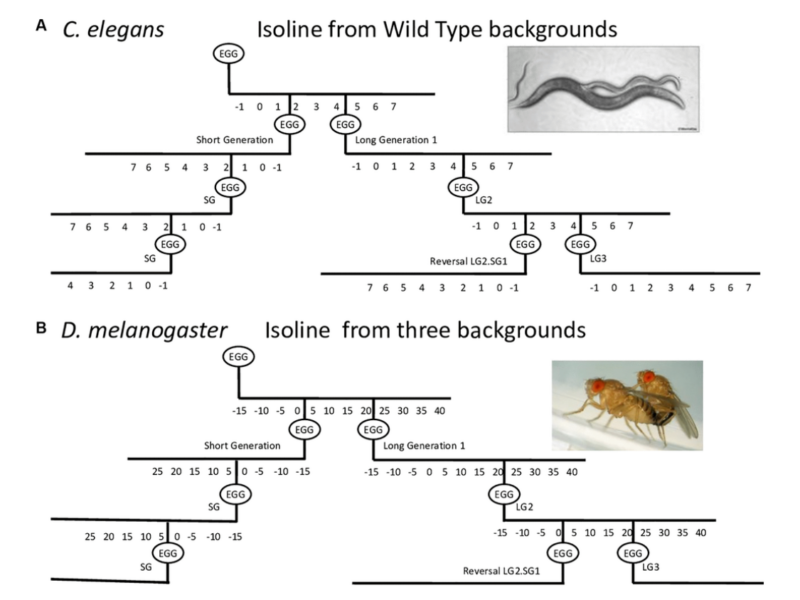
PRESS RELEASE: A new research paper was published in Aging’s Volume 15, Issue 21, entitled, “Parental age effect on the longevity and healthspan in Drosophila melanogaster and Caenorhabditis elegans.”
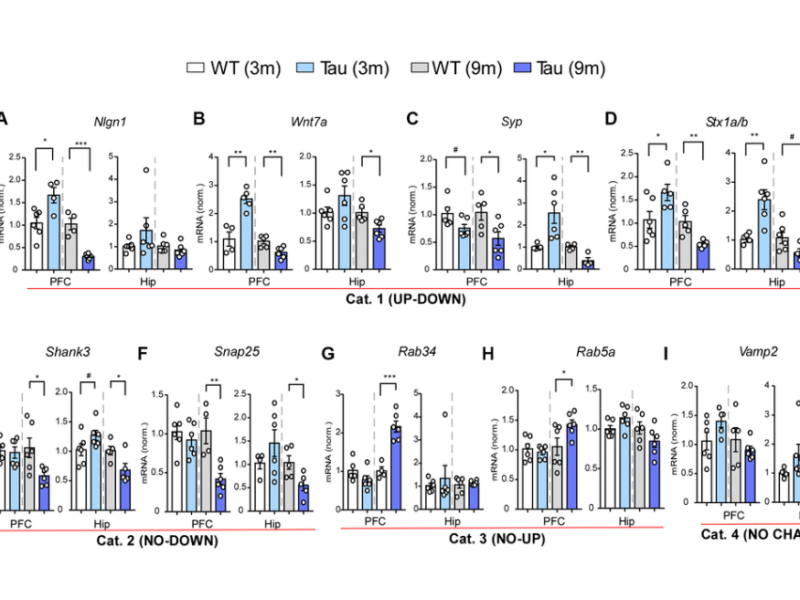
PRESS RELEASE: A new research paper was published on the cover of Aging’s Volume 15, Issue 21, entitled, “Longitudinal characterization of behavioral, morphological and transcriptomic changes in a tauopathy mouse model.”
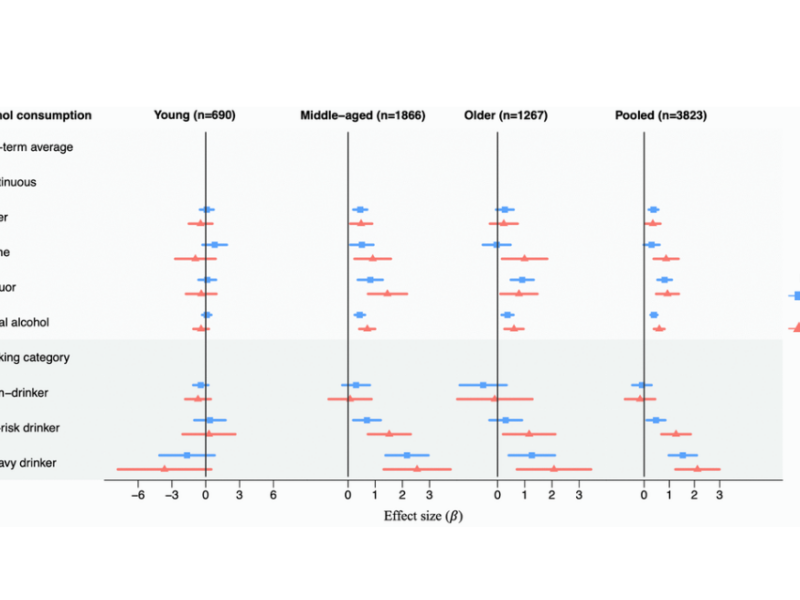
PRESS RELEASE: A new research paper was published in Aging’s Volume 15, Issue 20, entitled, “Alcohol consumption and epigenetic age acceleration across human adulthood.”
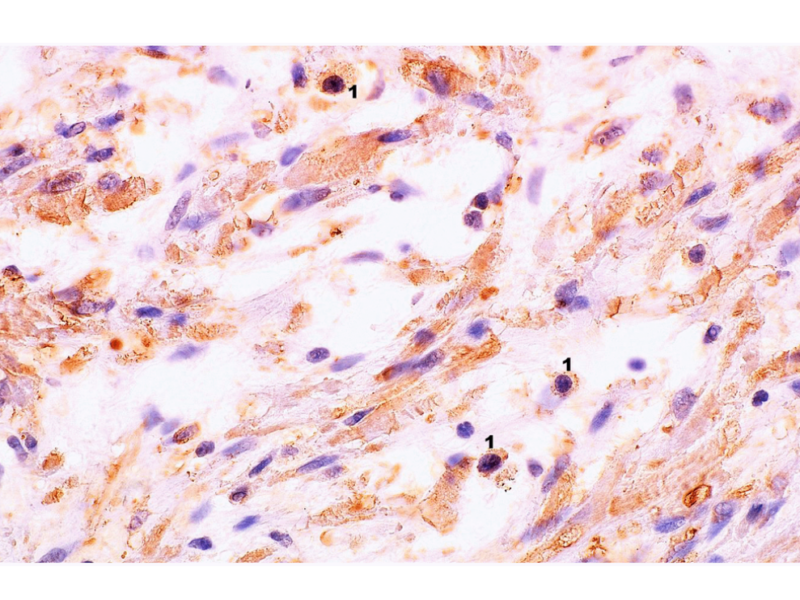
PRESS RELEASE: A new research paper was published in Aging’s Volume 15, Issue 20, entitled, “Tissue immunoexpression of IL-6 and IL-18 in aging men with BPH and MetS and their relationship with lipid parameters and gut microbiota-derived short chain fatty acids.”
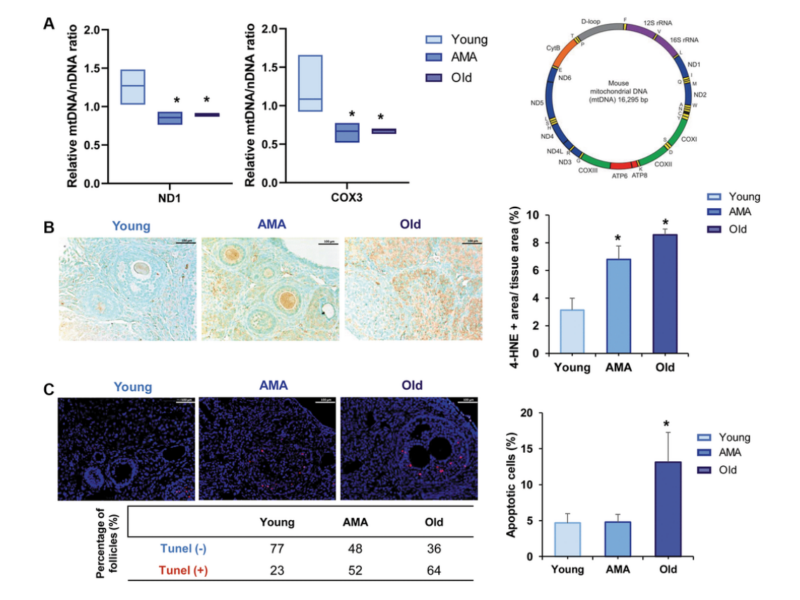
PRESS RELEASE: A new research paper was published in Aging’s Volume 15, Issue 20, entitled, “Deciphering reproductive aging in women using a NOD/SCID mouse model for distinct physiological ovarian phenotypes.”

PRESS RELEASE: A new research perspective was published in Aging’s Volume 15, Issue 20, entitled, “Cholinergic centro-cingulate network in Parkinson disease and normal aging.”