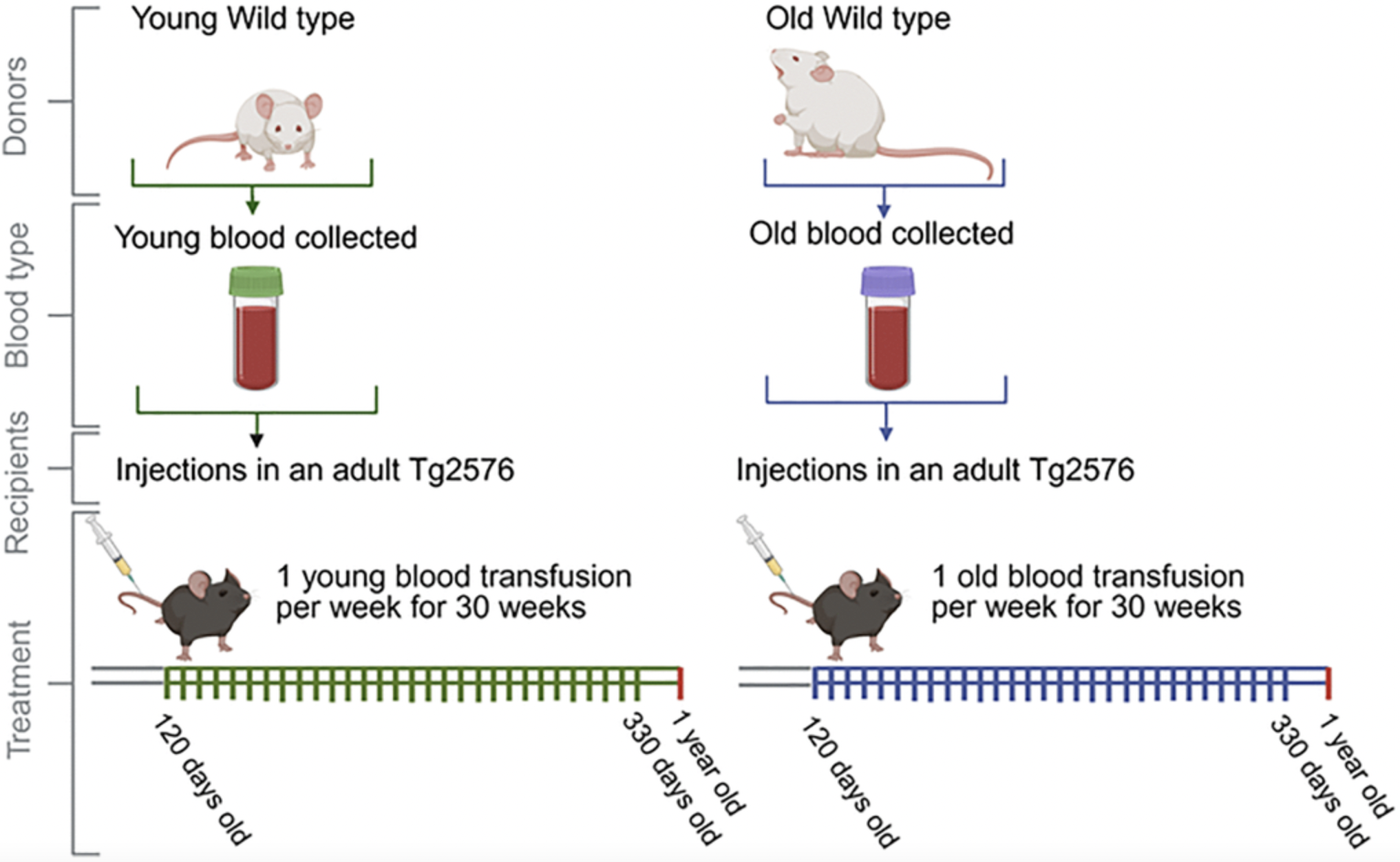
A new research paper was published in Volume 17, Issue 11 of Aging-US on September 12, 2025, titled “Infusion of blood from young and old mice modulates amyloid pathology.”
Aging-US Authors

A new research paper was published in Volume 17, Issue 10 of Aging-US on October 13, 2025, titled “Hospitalization with infections and risk of Dementia: a systematic review and meta-analysis.”
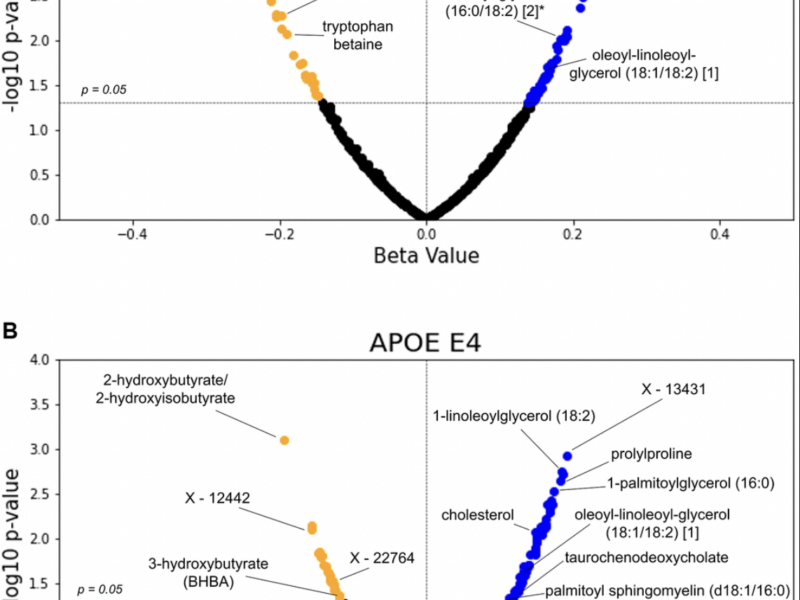
A new research paper was published in Aging (Aging-US) Volume 17, Issue 5, on May 3, 2025, titled “APOE genotype and biological age impact inter-omic associations related to bioenergetics.”
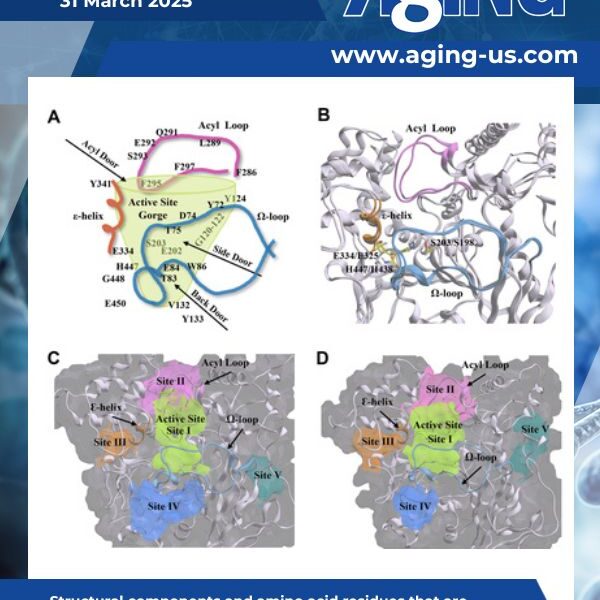
A new research paper was published in Aging (Aging-US) on March 29, 2025, as the cover of Volume 17, Issue 3, titled “Differential senolytic inhibition of normal versus Aβ-associated cholinesterases: implications in aging and Alzheimer’s disease.”

Cellular senescence is a hallmark of aging and the age-related condition, Alzheimer’s disease (AD). How senescence contributes to cholinergic and neuropathologic changes in AD remains uncertain. Furthermore, little is known about the relationship between senescence and cholinesterases (ChEs).
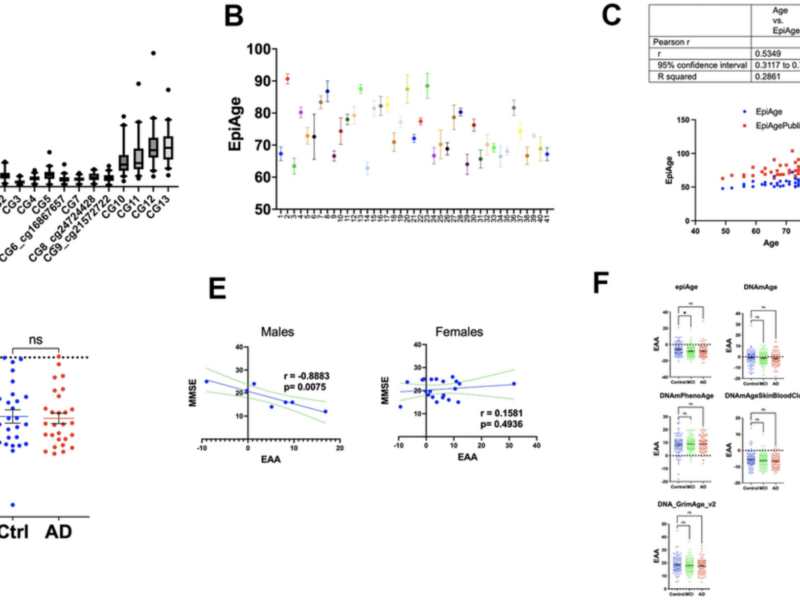
A new research paper was published in Aging (Aging-US) on January 22, 2025, in Volume 17, Issue 1, titled “EpiAge: a next-generation sequencing-based ELOVL2 epigenetic clock for biological age assessment in saliva and blood across health and disease.”
Dr. Moshe Szyf from EpiMedTech Global in Singapore discusses a research paper he co-authored that was published in Volume 17, Issue 1 of Aging (Aging-US), entitled “EpiAge: a next-generation sequencing-based ELOVL2 epigenetic clock for biological age assessment in saliva and blood across health and disease.”

A new priority research paper, featured as the cover of Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as “Aging (Albany NY)” and “Aging-US” by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 22, was published on December 29, 2024. The paper is titled “Cell-type specific epigenetic clocks to quantify biological age at cell-type resolution.”
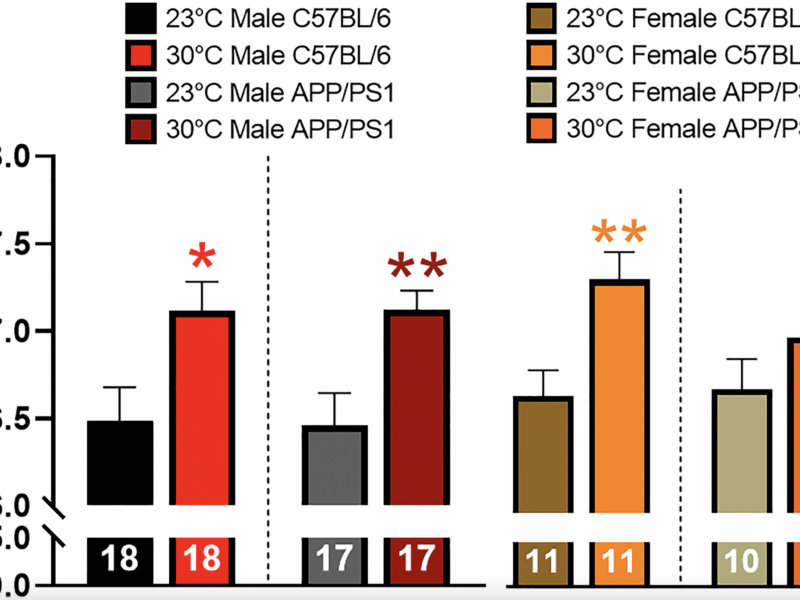
A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as “Aging (Albany NY)” and “Aging-US” by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 21 on November 29, 2024, entitled, “Thermotherapy has sexually dimorphic responses in APP/PS1 mice.”
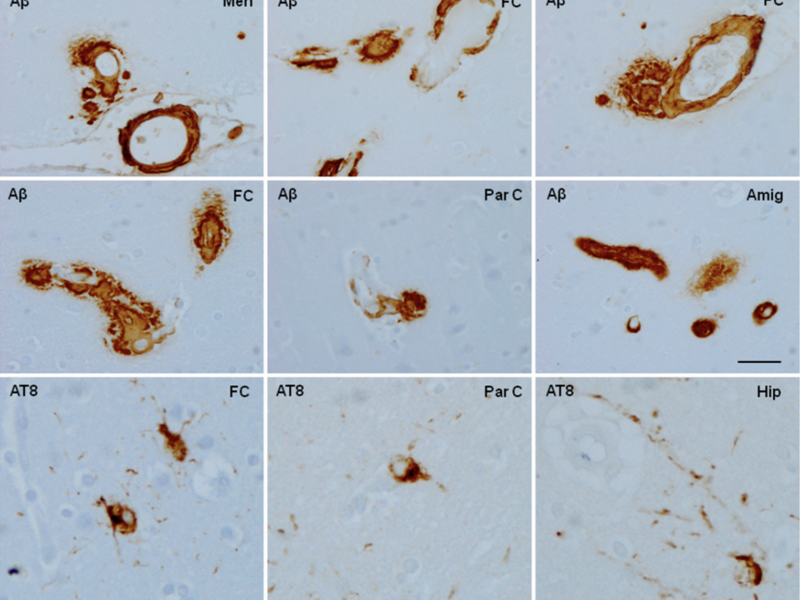
A new review was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as “Aging (Albany NY)” and “Aging-US” by Web of Science), on October 29, 2024, Volume 16, Issue 20, titled, ”Brain aging and Alzheimer’s disease, a perspective from non-human primates.“