PRESS RELEASE – A new editorial was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as “Aging (Albany NY)” and “Aging-US” by Web of Science), Volume 16, Issue 15 on July 19, 2024, entitled, “Physical fitness and lifestyles associated with biological aging.”
Aging-US Authors
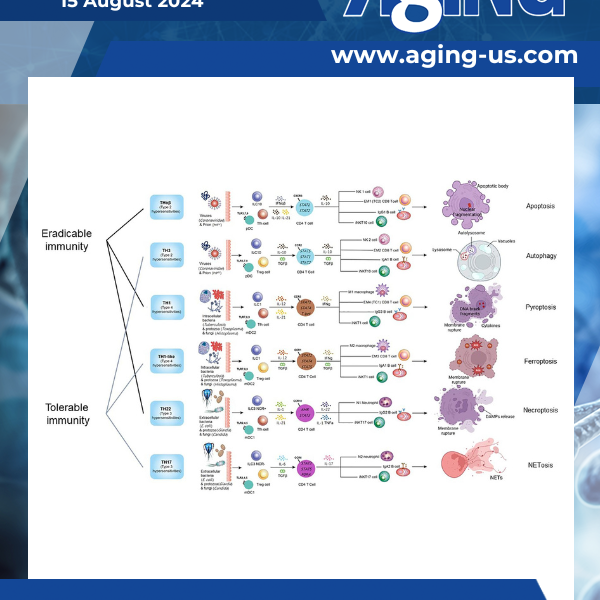
PRESS RELEASE – A new review was published as the cover paper of Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as “Aging (Albany NY)” and “Aging-US” by Web of Science), Volume 16, Issue 15, entitled, “Types of cell death and their relations to host immunological pathways.”
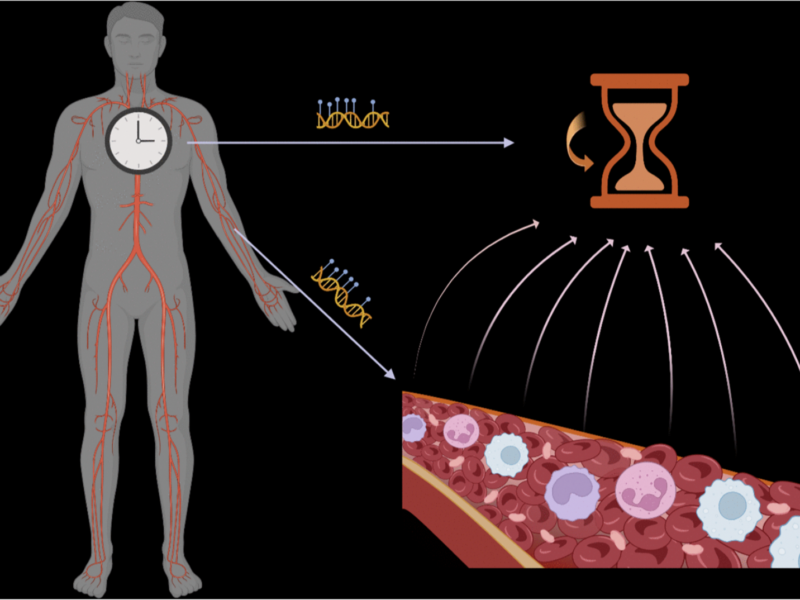
PRESS RELEASE – A new editorial was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as “Aging (Albany NY)” and “Aging-US” by Web of Science), Volume 16, Issue 14 on July 17, 2024, entitled, “Recalibrate concepts of epigenetic aging clocks in human health.”
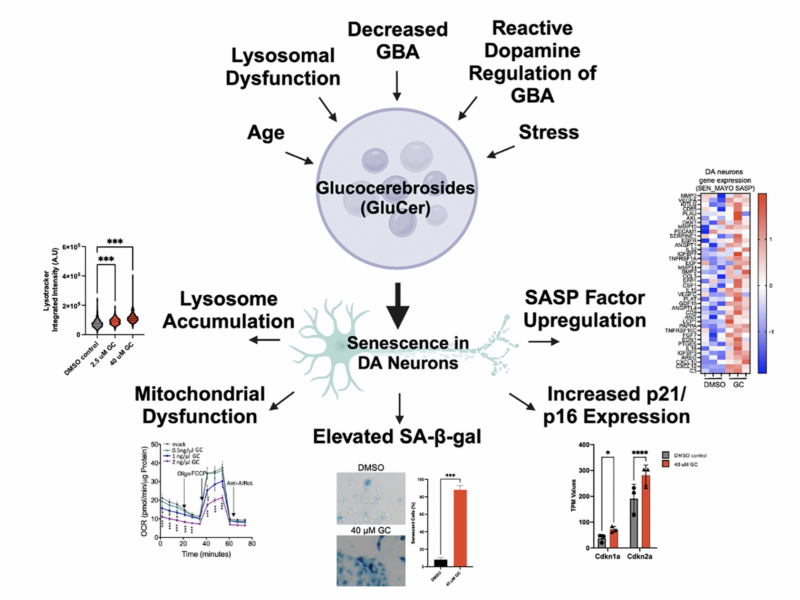
PRESS RELEASE – A new research perspective was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as “Aging (Albany NY)” and “Aging-US” by Web of Science), Volume 16, Issue 14 on July 19, 2024, entitled, “Lipid accumulation drives cellular senescence in dopaminergic neurons.”
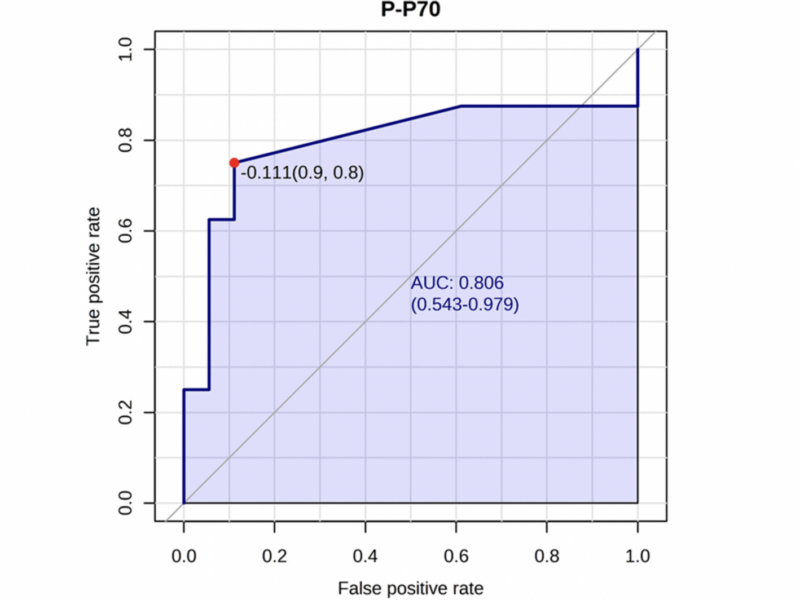
PRESS RELEASE: A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as “Aging (Albany NY)” and “Aging-US” by Web of Science), Volume 16, Issue 14 on July 26, 2024, entitled, “mTORC1 activation in presumed classical monocytes: observed correlation with human size variation and neuropsychiatric disease.”
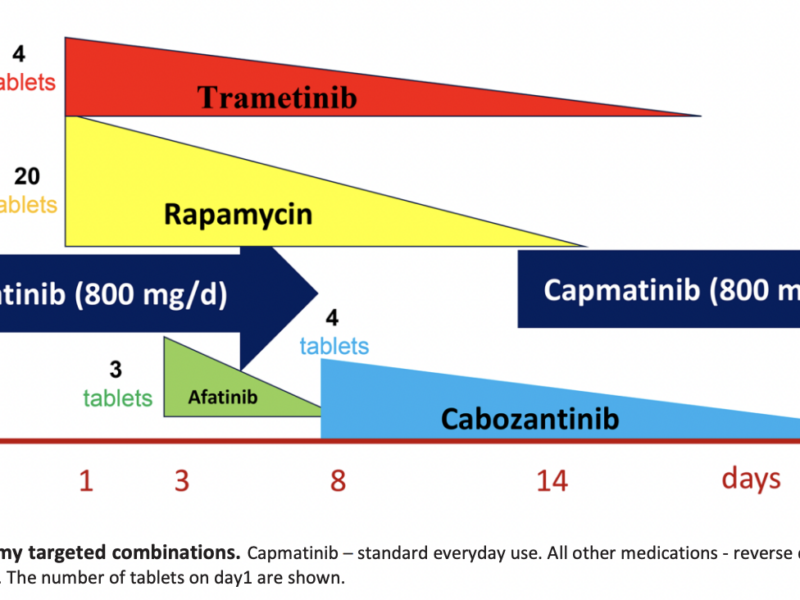
PRESS RELEASE – On July 28, 2024, Mikhail V. Blagosklonny M.D., Ph.D., from Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center published a new editorial in Volume 16, Issue 14 of Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as “Aging (Albany NY)” and “Aging-US” by Web of Science), entitled, “Targeted cancer therapy: the initial high concentration may slow down the selection for resistance.”
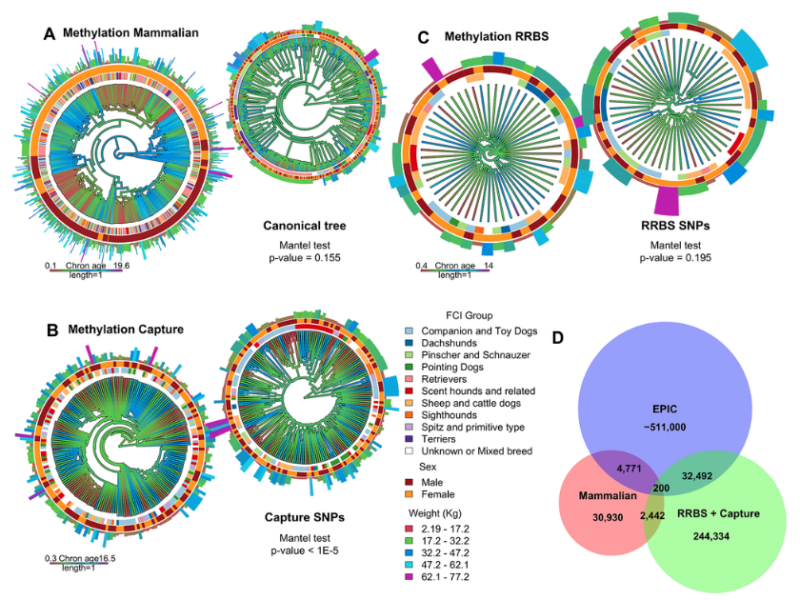
PRESS RELEASE: A new research paper was published in Aging’s Volume 16, Issue 13, entitled, “Co-analysis of methylation platforms for signatures of biological aging in the domestic dog reveals previously unexplored confounding factors.”
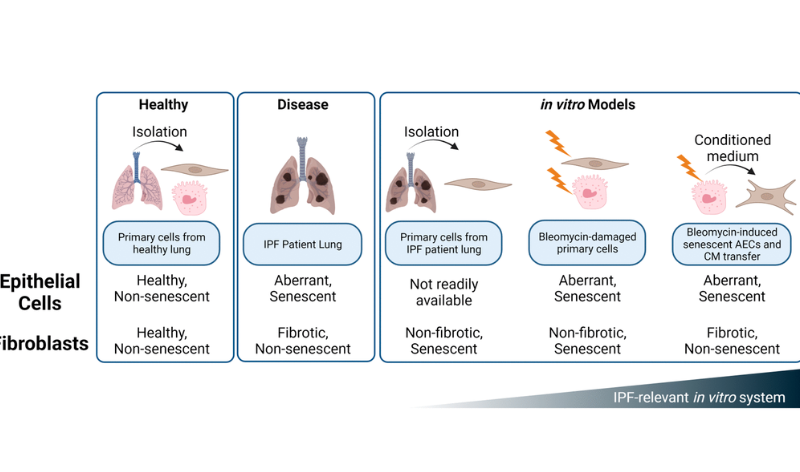
PRESS RELEASE: A new research paper was published in Aging’s Volume 16, Issue 13, entitled, “Modulating in vitro lung fibroblast activation via senolysis of senescent human alveolar epithelial cells.”
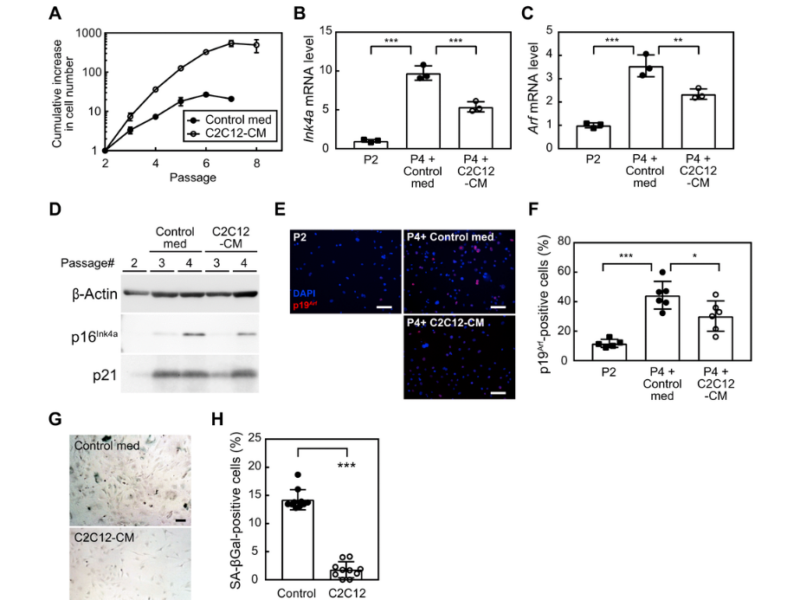
Roles of PEDF in Exercise-induced Suppression of Senescence and its Impact on Lung Pathology in Mice
PRESS RELEASE: A new research paper was published on the cover of Aging’s Volume 16, Issue 13, entitled, “Roles of pigment epithelium-derived factor in exercise-induced suppression of senescence and its impact on lung pathology in mice.”
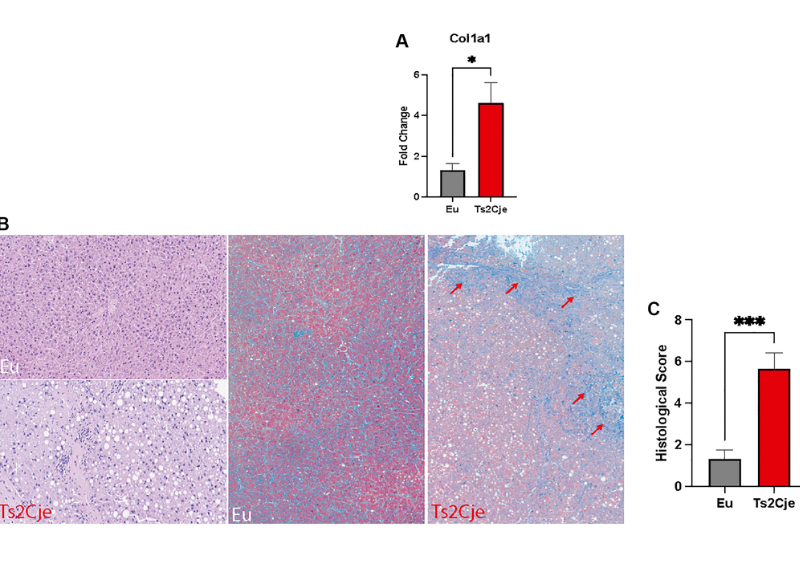
PRESS RELEASE: A new research paper was published in Aging’s Volume 16, Issue 12, entitled, “Aging exacerbates oxidative stress and liver fibrosis in an animal model of Down Syndrome.”
