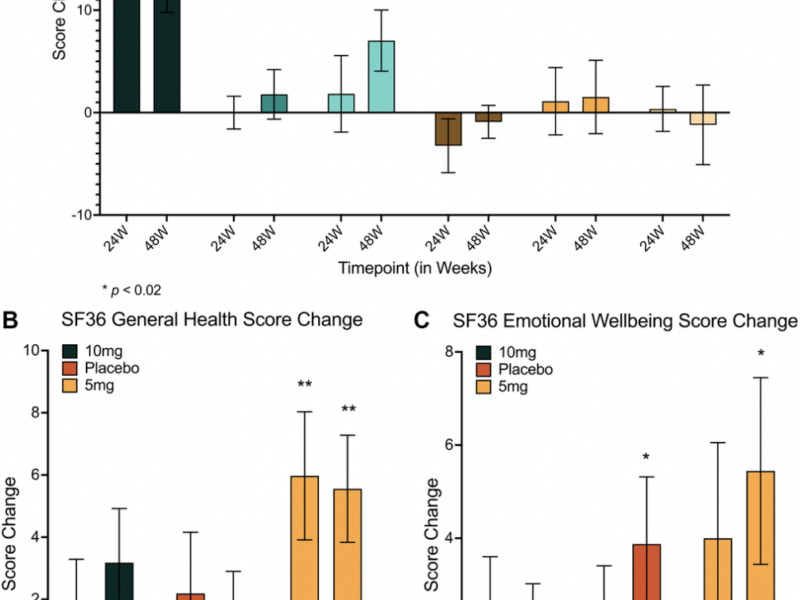
A new research paper was published in Aging (Aging-US) Volume 17, Issue 4, on April 4, 2025, titled “Influence of rapamycin on safety and healthspan metrics after one year: PEARL trial results.”
Aging (Aging-US) Authors
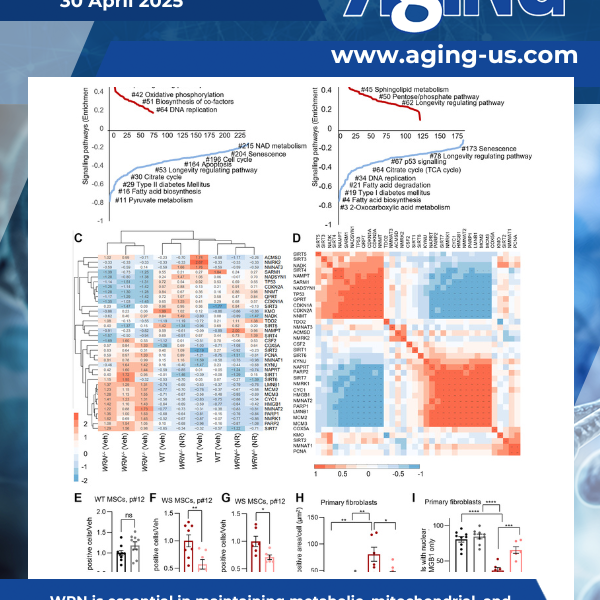
A new research paper was published in Aging (Aging-US) on April 2, 2025, as the cover of Volume 17, Issue 4, titled “Decreased mitochondrial NAD+ in WRN deficient cells links to dysfunctional proliferation.”
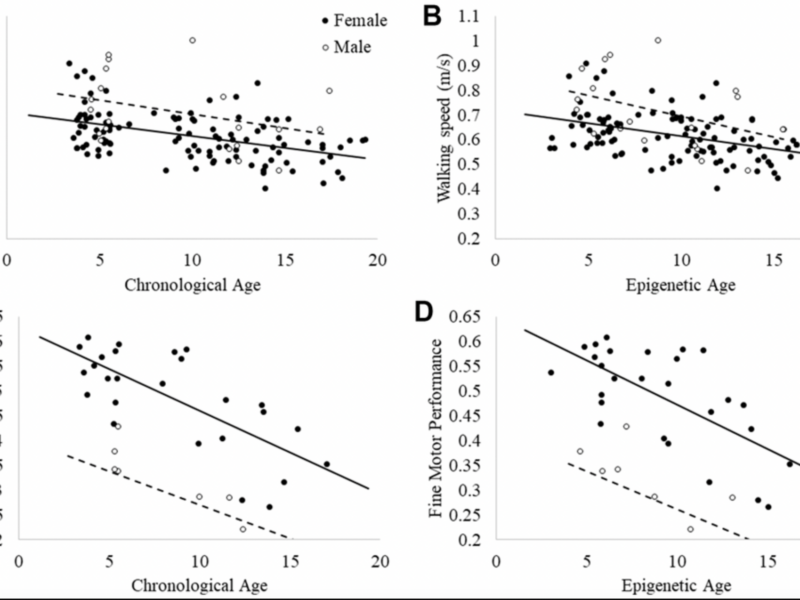
A new research paper was published in Aging (Aging-US) Volume 17, Issue 3, on March 18, 2025, titled “Epigenetic and accelerated age in captive olive baboons (Papio anubis), and relationships with walking speed and fine motor performance.”
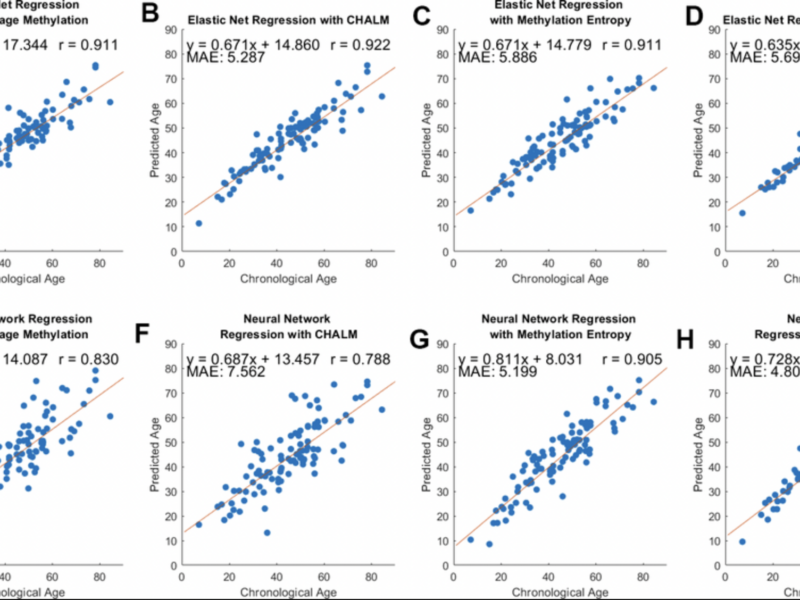
A new research paper was published in Aging (Aging-US) Volume 17, Issue 3, on March 12, 2025, titled “DNA methylation entropy is a biomarker for aging.”
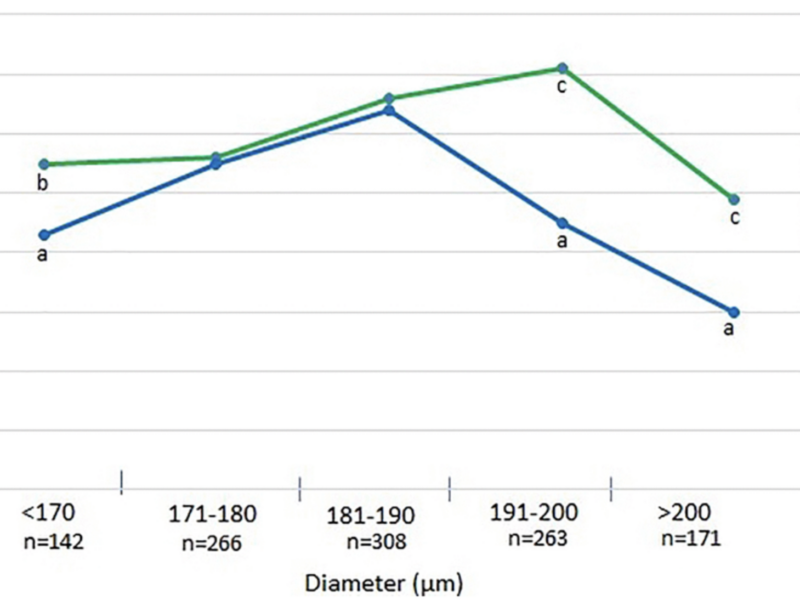
A new research paper was published in Aging (Aging-US) Volume 17, Issue 3, on March 5, 2025, titled “Reproductive aging, preimplantation genetic testing for aneuploidy, and the diameter of blastocysts: does size matter?”
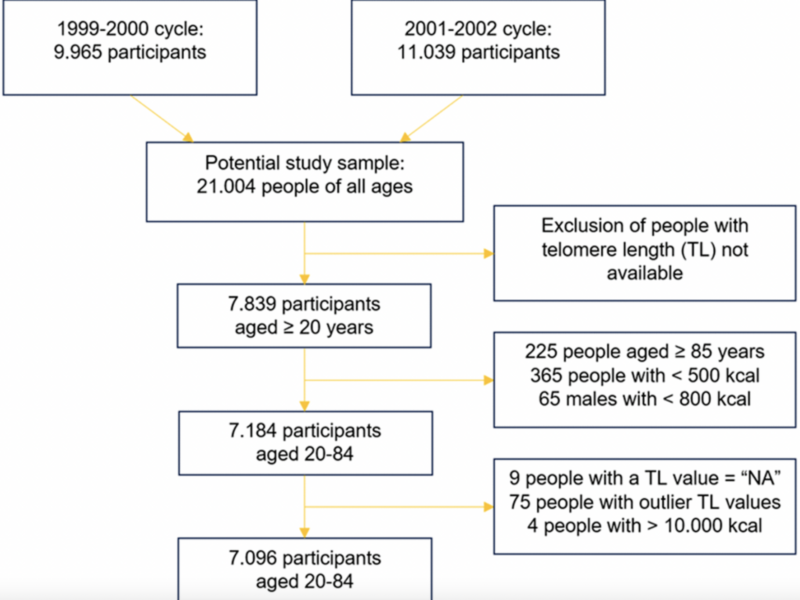
A new research paper was published in Aging (Aging-US) on January 29, 2025, in Volume 17, Issue 2, titled “Diet, lifestyle and telomere length: using Copula Graphical Models on NHANES data.”
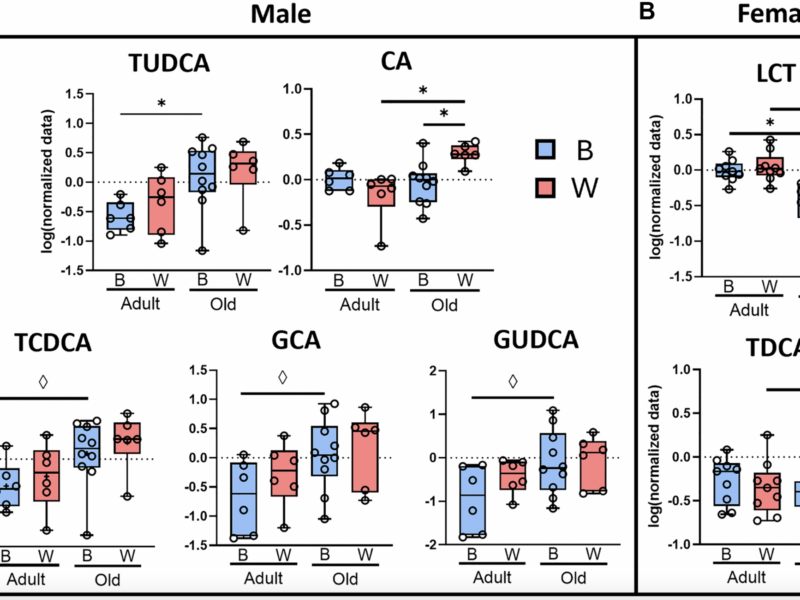
A new research paper was published in Aging (Aging-US) on February 27, 2025, in Volume 17, Issue 2, titled “Age, sex, and mitochondrial-haplotype influence gut microbiome composition and metabolites in a genetically diverse rat model.”
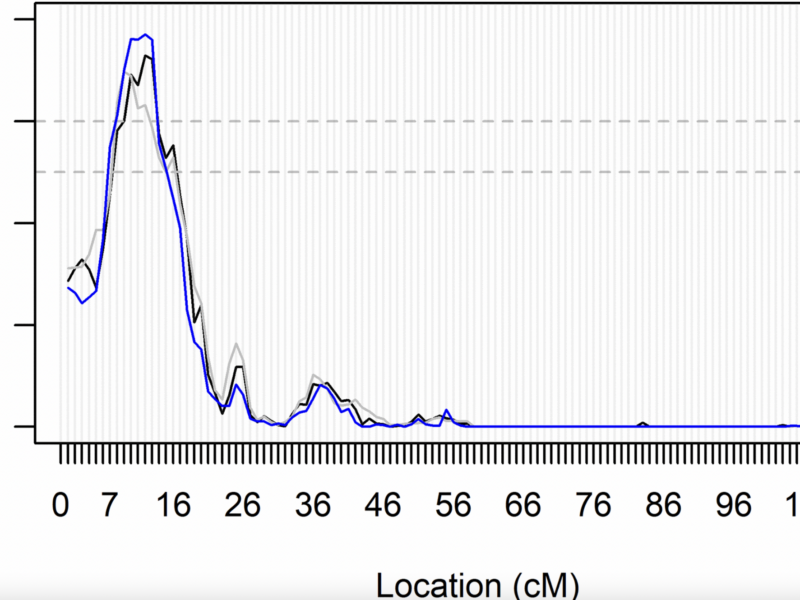
A new research paper was published in Aging (Aging-US) on February 25, 2025, Volume 17, Issue 2, titled “Epidemiology and genetic determination of measures of peripheral vascular health in the Long Life Family Study.”
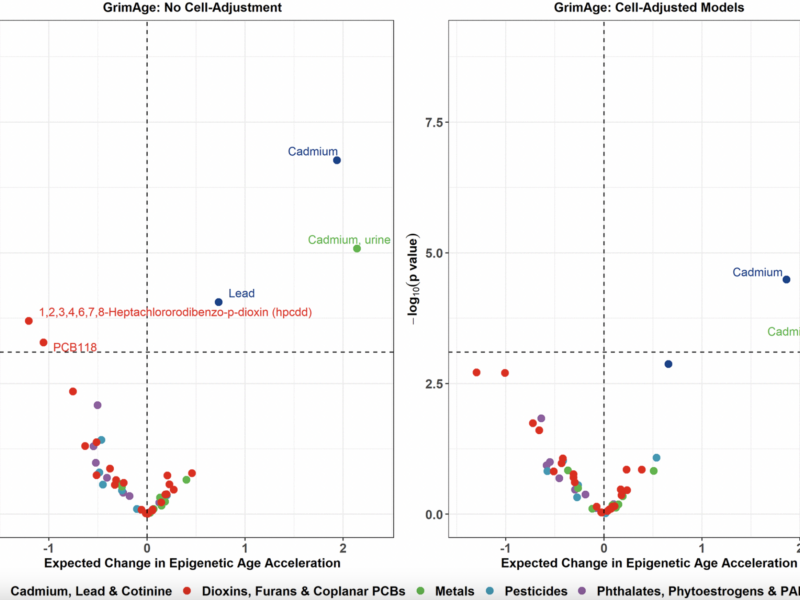
A new research paper was published in Aging (Aging-US) on February 11, 2025, Volume 17, Issue 2, titled “Exposome-wide association study of environmental chemical exposures and epigenetic aging in the national health and nutrition examination survey.”
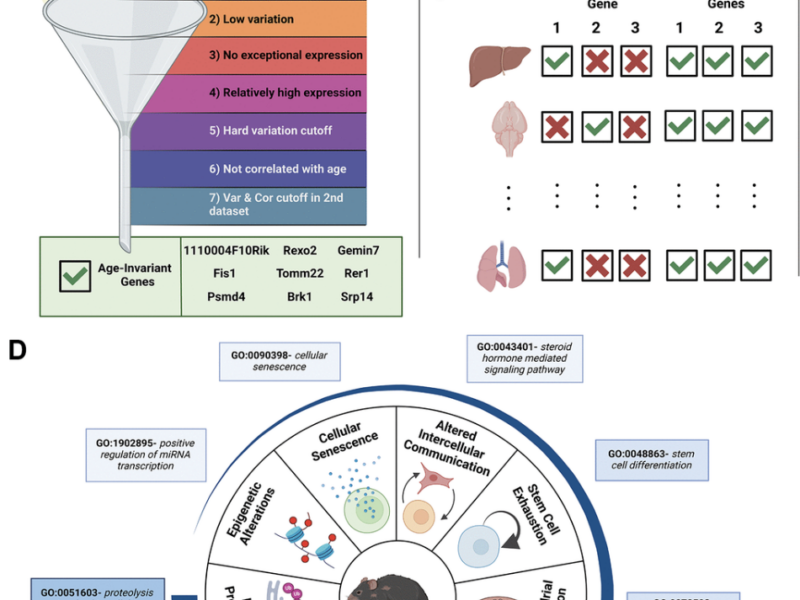
A new research paper was published in Aging (Aging-US) on January 27, 2025, in Volume 17, Issue 1, titled “Age-invariant genes: multi-tissue identification and characterization of murine reference genes.”