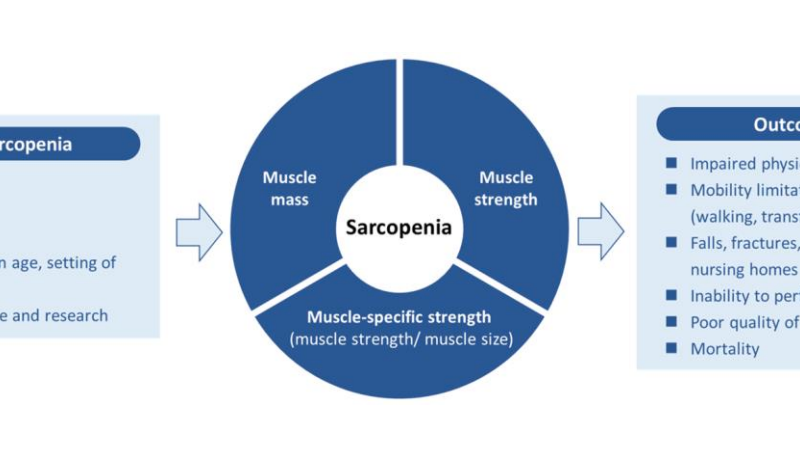
PRESS RELEASE: A new editorial paper was published in Aging’s Volume 16, Issue 11, entitled, “Global consensus for sarcopenia.”
Aging (Aging-US) Authors
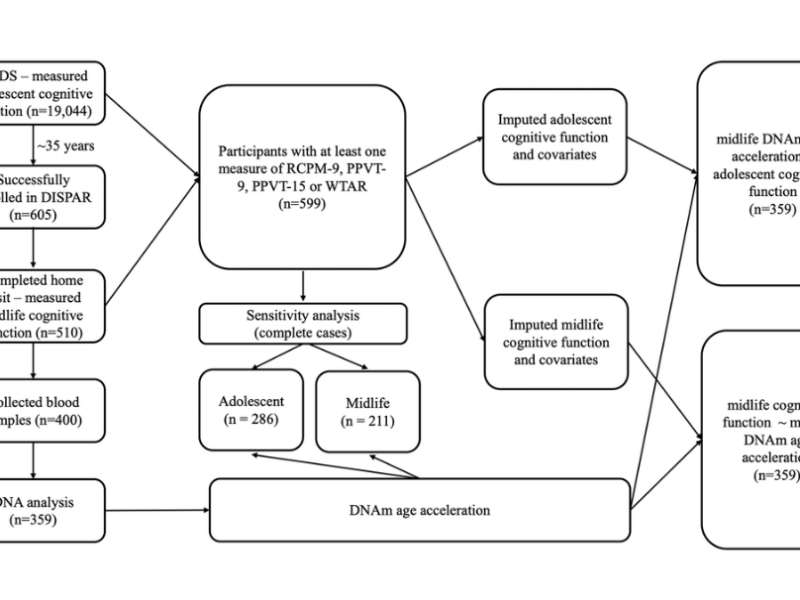
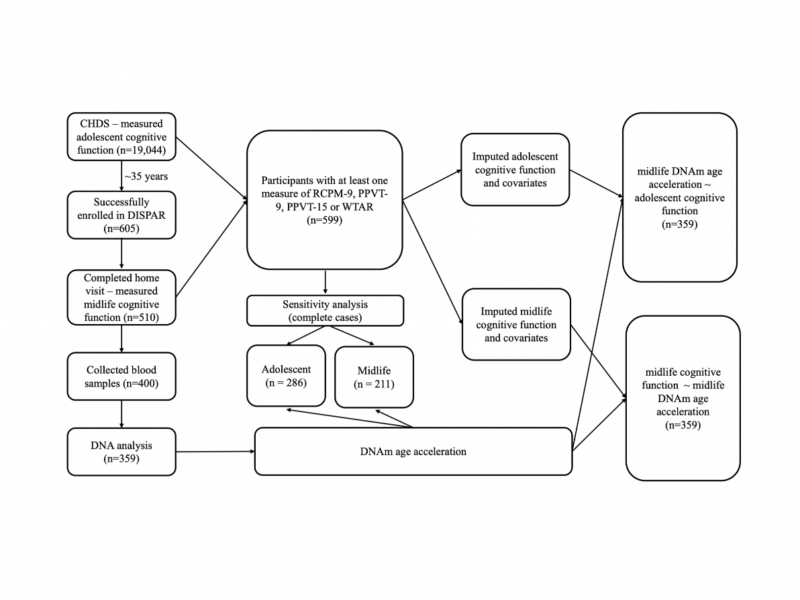
PRESS RELEASE: A new research paper was published in Aging’s Volume 16, Issue 11, entitled, “Associations of childhood, adolescence, and midlife cognitive function with DNA methylation age acceleration in midlife.”
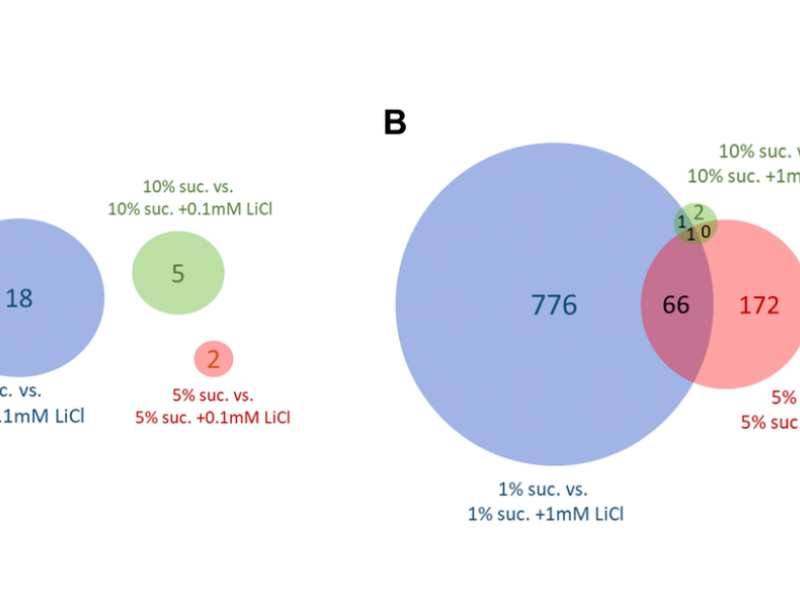
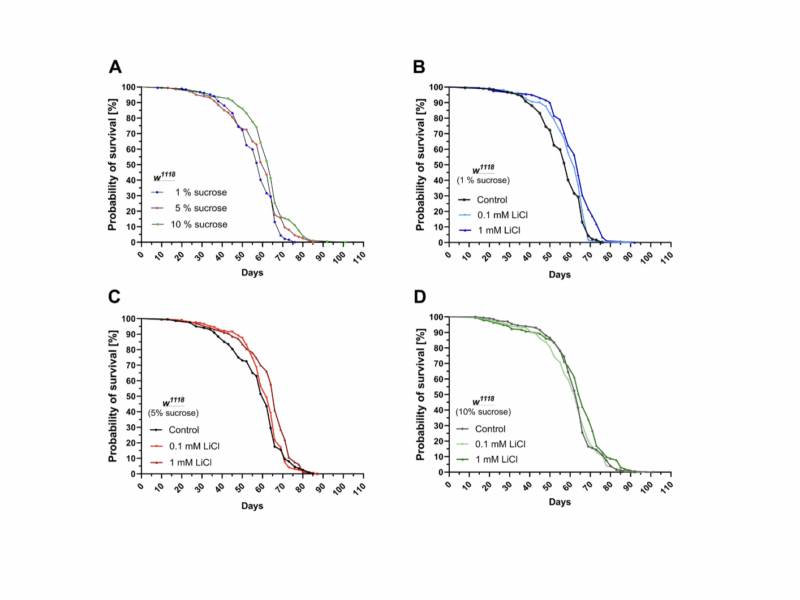
PRESS RELEASE: A new research paper was published in Aging’s Volume 16, Issue 11, entitled, “Dietary sucrose determines the regulatory activity of lithium on gene expression and lifespan in Drosophila melanogaster.”
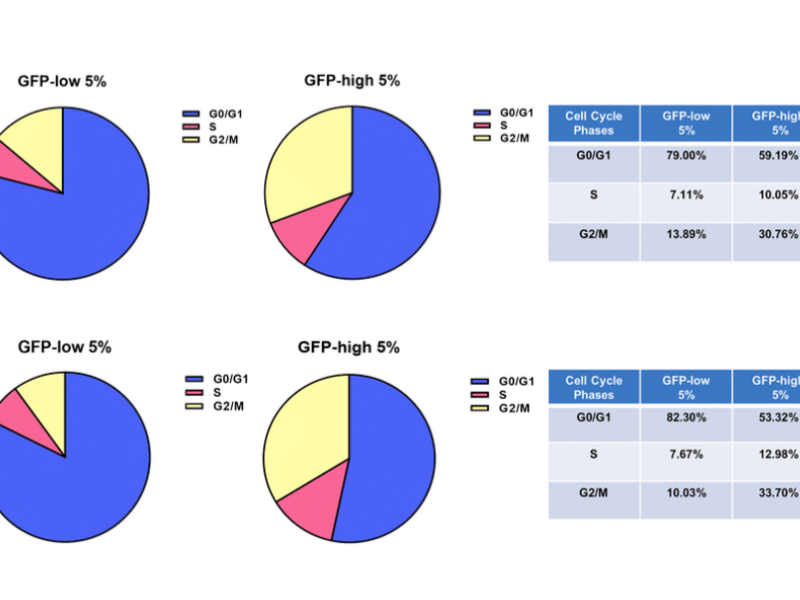
PRESS RELEASE: A new research paper was published on the cover of Aging’s Volume 16, Issue 11, entitled, “Mitophagy and cancer: role of BNIP3/BNIP3L as energetic drivers of stemness features, ATP production, proliferation, and cell migration.”
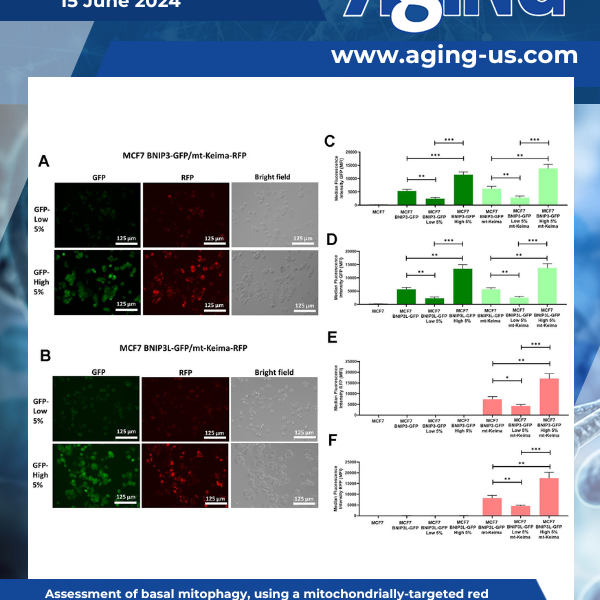
Mitophagy is a selective form of autophagy which permits the removal of dysfunctional or excess mitochondria. This occurs as an adaptative response to physiological stressors, such as hypoxia, nutrient deprivation, or DNA damage. Mitophagy is promoted by specific mitochondrial outer membrane receptors, among which are BNIP3 and BNIP3L.
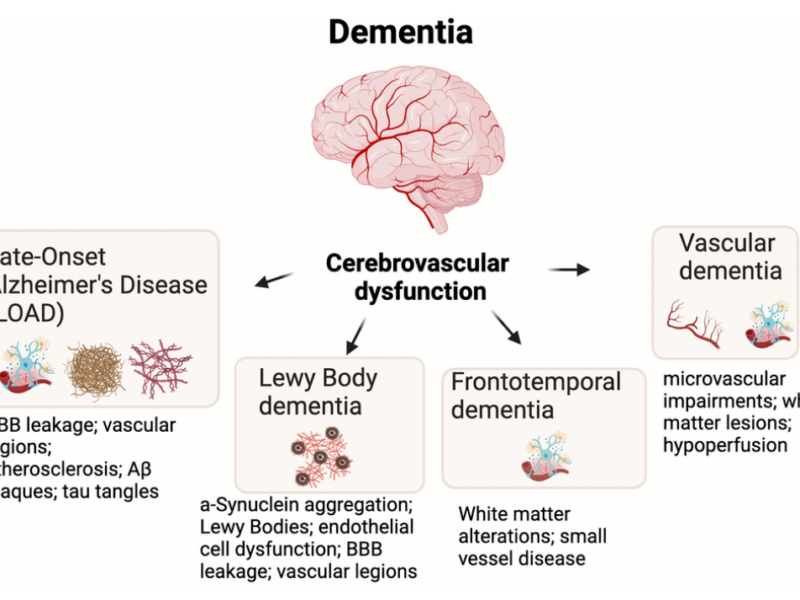
PRESS RELEASE: A new review was published in Aging’s Volume 16, Issue 10, entitled, “Peripheral vascular dysfunction and the aging brain.”

Aging is thrilled to sponsor Team Open Access again in the annual cycling event to end cancer: The Ride for Roswell.
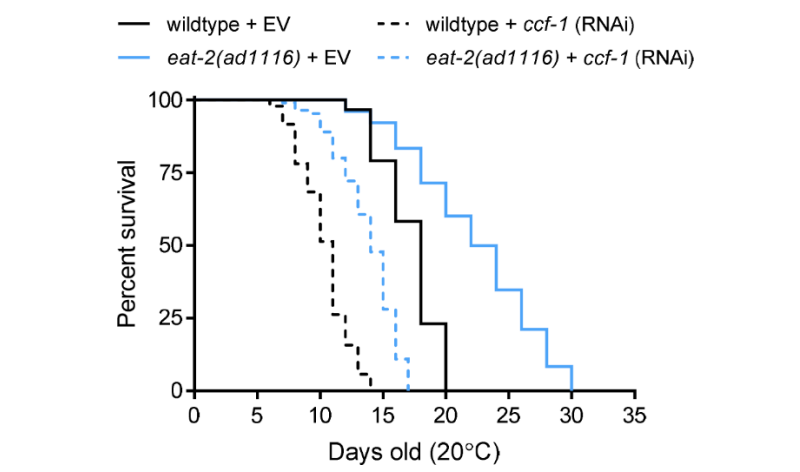
PRESS RELEASE: A new editorial paper was published in Aging’s Volume 16, Issue 10, entitled, “CCR4-NOT complex in stress resistance and longevity in C. elegans.”