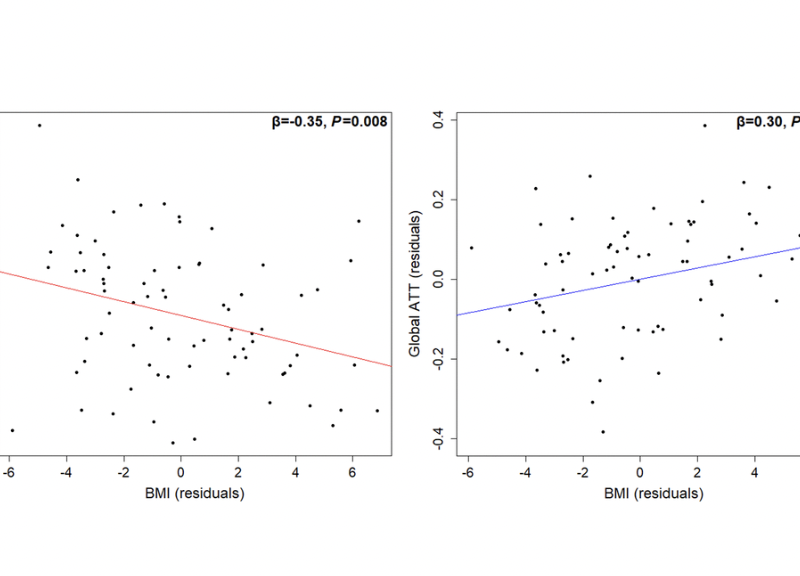
PRESS RELEASE – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as “Aging (Albany NY)” and “Aging-US” by Web of Science), Volume 16, Issue 18 on September 18, 2024, entitled, “Determinants of cerebral blood flow and arterial transit time in healthy older adults.”
Aging-US Authors
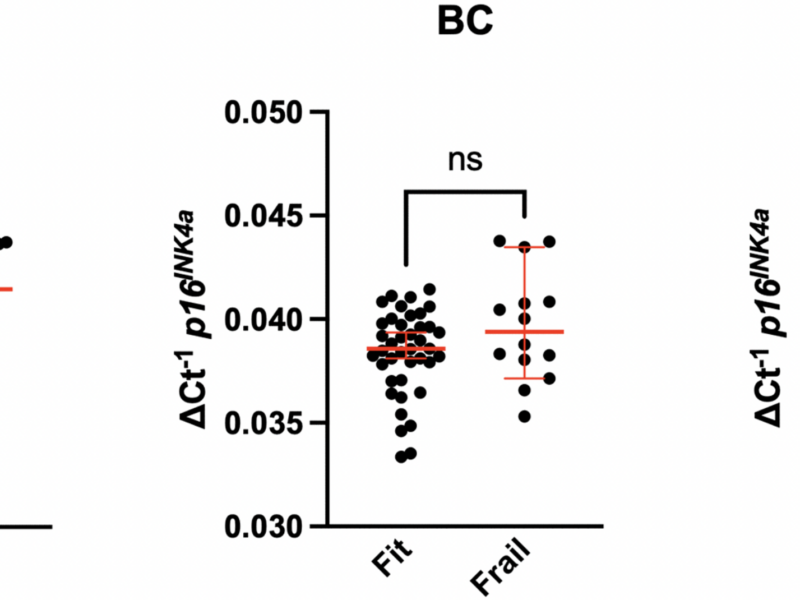
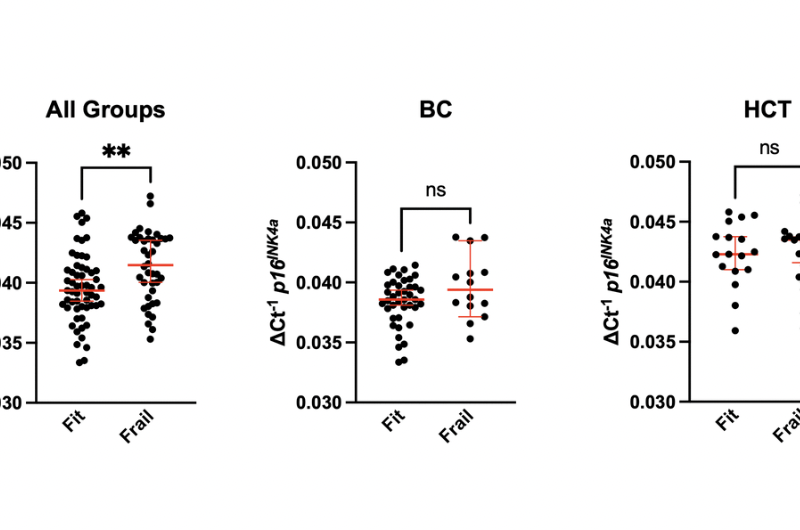
PRESS RELEASE – A new research paper was published on the in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as “Aging (Albany NY)” and “Aging-US” by Web of Science), Volume 16, Issue 18 on September 26, 2024, entitled, “Frailty and pre-frailty associated with long-term diminished physical performance and quality of life in breast cancer and hematopoietic cell transplant survivors.”
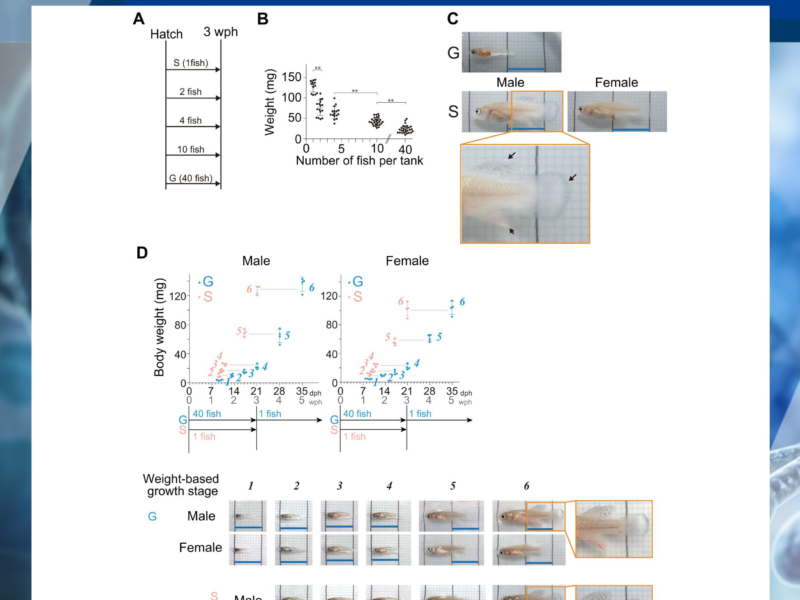
PRESS RELEASE – A new research paper was published on the cover of Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as “Aging (Albany NY)” and “Aging-US” by Web of Science), Volume 16, Issue 18 on September 16, 2024, entitled, “Single housing of juveniles accelerates early-stage growth but extends adult lifespan in African turquoise killifish.”

Within the same species, individuals exhibiting faster growth tend to have shorter lifespans, even if their fast growth arises from early-life pharmacological interventions. However, in vertebrates, the impact of the early-life environment on the growth rate and lifespan has not been fully elucidated.

Nadiyeh Rouhi from the Department of Physiology at the University of Mississippi Medical Center (UMMC), Jackson, MS, discusses an editorial she co-authored that was published by Aging (Aging-US) in Volume 16, Issue 16, titled “Cardiac Metabolism in the Elderly: Effects and Consequences.”
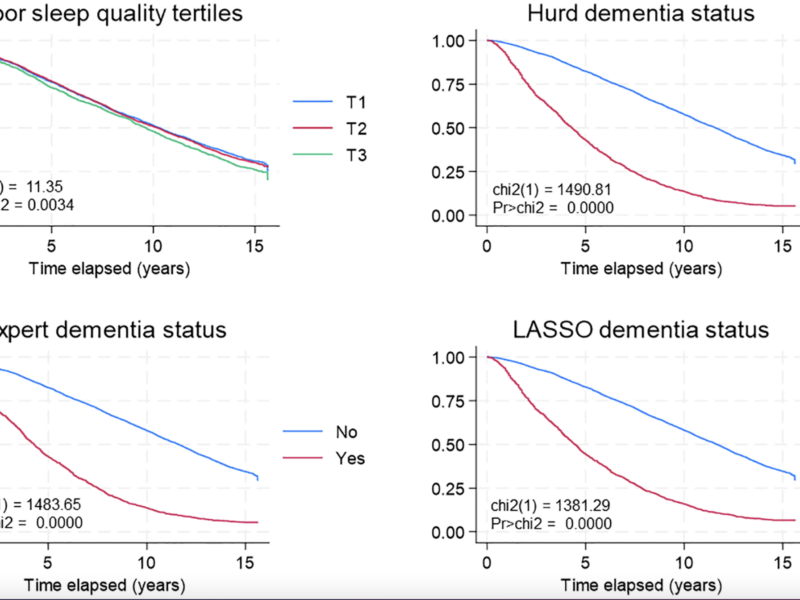
PRESS RELEASE – A new research paper titled, “Poor sleep quality, dementia status and their association with all-cause mortality among older US adults” was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as “Aging (Albany NY)” and “Aging-US” by Web of Science), Volume 16, Issue 17, on September 4, 2024.
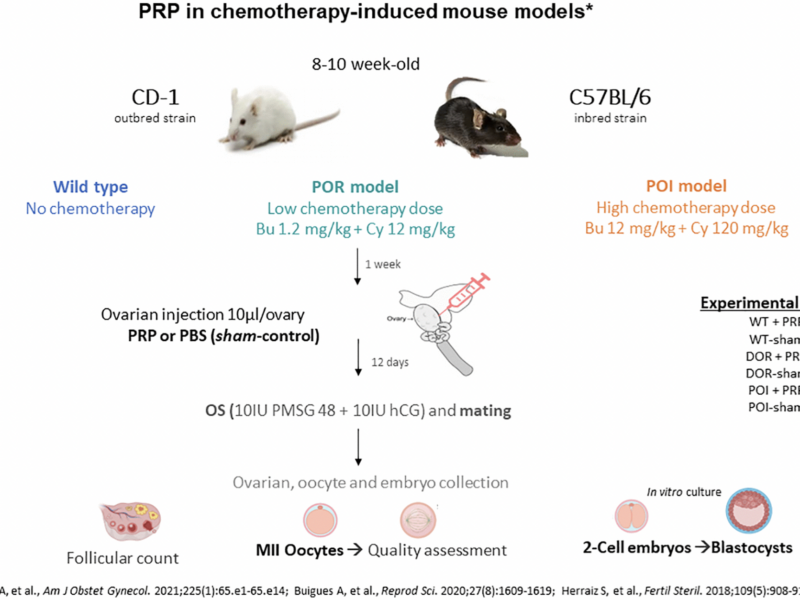
PRESS RELEASE – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as “Aging (Albany NY)” and “Aging-US” by Web of Science), Volume 16, Issue 17 on September 13, 2024, entitled, “Intraovarian PRP injection improves oocyte quality and early embryo development in mouse models of chemotherapy-induced diminished ovarian reserve.”
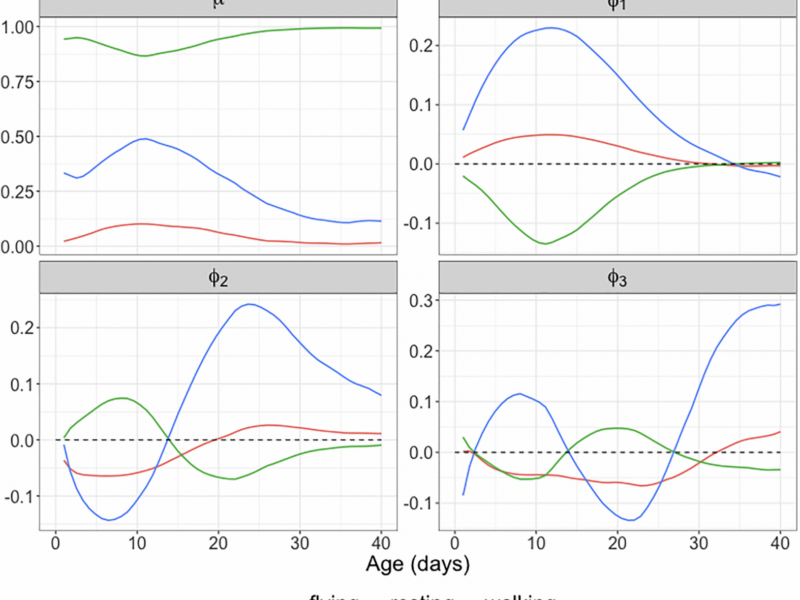
PRESS RELEASE – A new research perspective was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as “Aging (Albany NY)” and “Aging-US” by Web of Science), Volume 16, Issue 17 on September 9, 2024, entitled, “Longitudinal activity monitoring and lifespan: quantifying the interface.”